Second round statewide sentinel-based population survey for estimation of the burden of active infection and anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies in the general population of Karnataka, India, during January-February 2021
- PMID: 35721769
- PMCID: PMC8620812
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijregi.2021.10.008
Second round statewide sentinel-based population survey for estimation of the burden of active infection and anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies in the general population of Karnataka, India, during January-February 2021
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Second round statewide sentinel-based population survey for estimation of the burden of active infection and anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies in the general population of Karnataka, India, during January-February 2021" [IJID Regions Vol 1(2021) pages 107-116].IJID Reg. 2024 Jan 19;10:150. doi: 10.1016/j.ijregi.2024.01.001. eCollection 2024 Mar. IJID Reg. 2024. PMID: 38314395 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: Demonstrate the feasibility of using the existing sentinel surveillance infrastructure to conduct the second round of the serial cross-sectional sentinel-based population survey. Assess active infection, seroprevalence, and their evolution in the general population across Karnataka. Identify local variations for locally appropriate actions. Additionally, assess the clinical sensitivity of the testing kit used on account of variability of antibody levels in the population.
Methods: The cross-sectional study of 41,228 participants across 290 healthcare facilities in all 30 districts of Karnataka was done among three groups of participants (low, moderate, and high-risk). The geographical spread was sufficient to capture local variations. Consenting participants were subjected to real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) testing, and antibody (IgG) testing. Clinical sensitivity was assessed by conducting a longitudinal study among participants identified as COVID-19 positive in the first survey round.
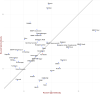
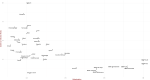
Results: Overall weighted adjusted seroprevalence of IgG was 15.6% (95% CI: 14.9-16.3), crude IgG prevalence was 15.0% and crude active infection was 0.5%. Statewide infection fatality rate (IFR) was estimated as 0.11%, and COVID-19 burden estimated between 26.1 to 37.7% (at 90% confidence). Further, Cases-to-infections ratio (CIR) varied 3-35 across units and IFR varied 0.04-0.50% across units. Clinical sensitivity of the IgG ELISA test kit was estimated as ≥38.9%.
Conclusion: We demonstrated the feasibility and simplicity of sentinel-based population survey in measuring variations in subnational and local data, useful for locally appropriate actions in different locations. The sentinel-based population survey thus helped identify districts that needed better testing, reporting, and clinical management. The state was far from attaining natural immunity during the survey and hence must step up vaccination coverage and enforce public health measures to prevent the spread of COVD-19.
Keywords: Karnataka; SARS-CoV-2; clinical sensitivity; sentinel survey; serosurvey.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Adiga, Aniruddha, Siva Athreya, Bryan Lewis, Madhav V Marathe, Nihesh Rathod, Rajesh Sundaresan, Samarth Swarup, Srinivasan Venkatramanan, and Sarath Yasodharan. 2021. 'Strategies to Mitigate COVID-19 Resurgence Assuming Immunity Waning: A Study for Karnataka, India', MedRxiv.
-
- Babu Giridhara R, Sundaresan Rajesh, Athreya Siva, Akhtar Jawaid, Pandey Pankaj Kumar, Maroor Parimala S, Rajagopal Padma M, Lalitha R, Shariff Mohammed, Krishnappa Lalitha. 'The burden of active infection and anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies in the general population: Results from a statewide sentinel-based population survey in Karnataka, India'. International Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2021;108:27–36. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cervia Carlo, Nilsson Jakob, Zurbuchen Yves, Valaperti Alan, Schreiner Jens, Wolfensberger Aline, Raeber Miro E, Adamo Sarah, Weigang Sebastian, Emmenegger Marc. Systemic and mucosal antibody responses specific to SARS-CoV-2 during mild versus severe COVID-19. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2021;147:545–557. e9. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

