Ten public health strategies to control the Covid-19 pandemic: the Saudi Experience
- PMID: 35721774
- PMCID: PMC8447545
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijregi.2021.09.003
Ten public health strategies to control the Covid-19 pandemic: the Saudi Experience
Abstract
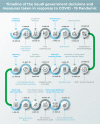
Saudi Arabia plays an important strategic role within the Middle East and afar because of its geographical location, and being the host of one of the largest annual religious mass gatherings in the world "The Hajj". During the recent coronavirus pandemic, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) developed a multisectoral plan that adopted multiple measures to limit the spread of Covid-19 transmission both domestically and internationally. In this article, we review all public health related policy decisions from the Saudi Ministry of Health, other government departments, and the private sector that contributed to limiting the severe consequences from Covid-19. Ten effective strategies are outlined and the challenges related to their implementation are explored. The strategies include: 1. Quarantine and travel restriction, 2. Expansion of serological screening, 3. Mask wearing (covering the face and nose) and social distancing, 4. Preparation of hospitals to deal with the influx of coronavirus cases, 5. Use of artificial intelligence, 6.Public assurance, 7.Removal of slum areas and re housing of its inhabitants, 8. Cancellation of the Hajj season, 9. Economic stimulus packages to safeguard the economy, and 10. fair and priority driven vaccine distribution. Conclusion: The government of Saudi Arabia demonstrated responsibility at the highest level to prioritize the safety and well-being of its citizens and residents. Rapid early response to the pandemic warnings, extensive experience in previous epidemics and in mass gathering medicine, wise management of healthcare resources, and unprecedented harmonization of governmental and private sectors were significant factors for this success.
Keywords: Covid_19; Pandemic; Saudi Arabia; control; experience; precautions; strategies.
© 2021 The Authors.
Figures


References
-
- Abusaaq H. Economic implications of Covid-19 on Saudi Arabia; 2020. Available from: https://home.kpmg/sa/en/home/insights/2020/04/economic-implications-of-c.... [Accessed 9 April 2020].
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

