Identification of Type 2 Diabetes Biomarkers From Mixed Single-Cell Sequencing Data With Feature Selection Methods
- PMID: 35721855
- PMCID: PMC9201257
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.890901
Identification of Type 2 Diabetes Biomarkers From Mixed Single-Cell Sequencing Data With Feature Selection Methods
Abstract
Diabetes is the most common disease and a major threat to human health. Type 2 diabetes (T2D) makes up about 90% of all cases. With the development of high-throughput sequencing technologies, more and more fundamental pathogenesis of T2D at genetic and transcriptomic levels has been revealed. The recent single-cell sequencing can further reveal the cellular heterogenicity of complex diseases in an unprecedented way. With the expectation on the molecular essence of T2D across multiple cell types, we investigated the expression profiling of more than 1,600 single cells (949 cells from T2D patients and 651 cells from normal controls) and identified the differential expression profiling and characteristics at the transcriptomics level that can distinguish such two groups of cells at the single-cell level. The expression profile was analyzed by several machine learning algorithms, including Monte Carlo feature selection, support vector machine, and repeated incremental pruning to produce error reduction (RIPPER). On one hand, some T2D-associated genes (MTND4P24, MTND2P28, and LOC100128906) were discovered. On the other hand, we revealed novel potential pathogenic mechanisms in a rule manner. They are induced by newly recognized genes and neglected by traditional bulk sequencing techniques. Particularly, the newly identified T2D genes were shown to follow specific quantitative rules with diabetes prediction potentials, and such rules further indicated several potential functional crosstalks involved in T2D.
Keywords: Monte Carlo feature selection; RIPPER; single-cell sequencing; support vector machine; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Pan and Cai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

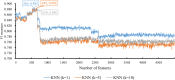
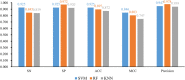

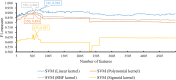
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

