Gadolinium-ethoxybenzyl-diethylenetriamine penta-acetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for evaluating fibrosis regression in chronic hepatitis C patients after direct-acting antiviral
- PMID: 35721884
- PMCID: PMC9157620
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i20.2214
Gadolinium-ethoxybenzyl-diethylenetriamine penta-acetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for evaluating fibrosis regression in chronic hepatitis C patients after direct-acting antiviral
Abstract
Background: Direct acting antiviral (DAA) therapy has enabled hepatitis C virus infection to become curable, while histological changes remain uncontained. Few valid non-invasive methods can be confirmed for use in surveillance. Gadolinium-ethoxybenzyl-diethylenetriamine penta-acetic acid (Gd-EOB-DTPA) is a liver-specific magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast, related to liver function in the hepatobiliary phase (HBP). Whether Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI can be used in the diagnosis and follow up of hepatic fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C (CHC) has not been investigated.
Aim: To investigate the diagnostic and follow-up values of Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI for hepatic histology in patients with CHC.
Methods: Patients with CHC were invited to undergo Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI and liver biopsy before treatment, and those with paired qualified MRI and liver biopsy specimens were included. Transient elastography (TE) and blood tests were also arranged. Patients treated with DAAs who achieved 24-wk sustained virological response (SVR) underwent Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI and liver biopsy again. The signal intensity (SI) of the liver and muscle were measured in the unenhanced phase (UEP) (SIUEP-liver, SIUEP-muscle) and HBP (SIHBP-liver, SIHBP-muscle) via MRI. The contrast enhancement index (CEI) was calculated as [(SIHBP-liver/SIHBP-muscle)]/[(SIUEP-liver/SIUEP-muscle)]. Liver stiffness measurement (LSM) was confirmed with TE. Serologic markers, aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index (APRI) and Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4), were also calculated according to blood tests. The grade of inflammation and stage of fibrosis were evaluated with the modified histology activity index (mHAI) and Ishak fibrosis score, respectively. Fibrosis regression was defined as a ≥ 1-point decrease in the Ishak fibrosis score. The correlation between the CEI and liver pathology was evaluated. The diagnostic and follow-up values of the CEI, LSM, and serologic markers were compared.
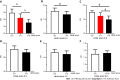
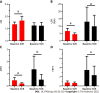
Results: Thirty-nine patients with CHC were enrolled [average age, 42.3 ± 14.4 years; 20/39 (51.3%) male]. Twenty-one enrolled patients had eligible paired Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI and liver tissues after achieving SVR. The mHAI median significantly decreased after SVR [baseline 6.0 (4.5-13.5) vs SVR 2.0 (1.5-5.5), Z = 3.322, P = 0.017], but the median stage of fibrosis did not notably change (P > 0.05). Sixty pairs of qualified MRI and liver tissue samples were available for use to analyze the relationship between the CEI and hepatic pathology. The CEI was negatively correlated with the mHAI (r = -0.56, P < 0.001) and Ishak score (r = -0.69, P < 0.001). Further stratified analysis showed that the value of the CEI decreased with the progression of the stage of fibrosis rather than with the grade of necroinflammation. For patients with Ishak score ≥ 5, the areas under receiver operating characteristics curve of the CEI, LSM, APRI, and FIB-4 were approximately at baseline, 0.87-0.93, and after achieving SVR, 0.83-0.91. The CEI cut-off value was stable (baseline 1.58 and SVR 1.59), but those of the APRI (from 1.05 to 0.24), FIB-4 (from 1.78 to 1.28), and LSM (from 10.8 kpa to 7.1 kpa) decreased dramatically. The APRI and FIB-4 cannot be used as diagnostic means for SVR in patients with Ishak score ≥ 3 (P > 0.05). Seven patients achieved fibrosis regression after achieving SVR. In these patients, the CEI median increased (from 1.71 to 1.83, Z = -1.981, P = 0.048) and those of the APRI (from 1.71 to 1.83, Z = -2.878, P = 0.004) and LSM (from 6.6 to 4.8, Z = -2.366, P = 0.018) decreased. However, in patients without fibrosis regression, the medians of the APRI, FIB-4, and LSM also changed significantly (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI has good diagnostic value for staging fibrosis in patients with CHC. It can be used for fibrotic-change monitoring post SVR in patients with CHC treated with DAAs.
Keywords: Contrast enhancement index; Direct acting antiviral; Fibrosis regression; Gadolinium-ethoxybenzyl-diethylenetriamine penta-acetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging; Hepatitis C virus; Sustained virological response.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Prof. Rao reports grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC), No. 81870406, and Beijing Natural Science Foundation, No. 7182174 during the conduct of the study.
Figures

References
-
- WHO Global hepatitis report, 2017. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2017. [cited 10 October 2021]. Available from: https://www.who.int/
-
- Global Burden of Disease Study 2013 Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;386:743–800. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lohmann V, Bartenschlager R. Indelibly Stamped by Hepatitis C Virus Infection: Persistent Epigenetic Signatures Increasing Liver Cancer Risk. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:2130–2133. - PubMed
-
- Knop V, Hoppe D, Welzel T, Vermehren J, Herrmann E, Vermehren A, Friedrich-Rust M, Sarrazin C, Zeuzem S, Welker MW. Regression of fibrosis and portal hypertension in HCV-associated cirrhosis and sustained virologic response after interferon-free antiviral therapy. J Viral Hepat. 2016;23:994–1002. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

