Direct Crystallization Resolution of Racemates Enhanced by Chiral Nanorods: Experimental, Statistical, and Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies
- PMID: 35722018
- PMCID: PMC9202296
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.2c01596
Direct Crystallization Resolution of Racemates Enhanced by Chiral Nanorods: Experimental, Statistical, and Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies
Abstract
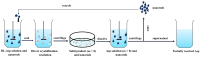
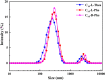
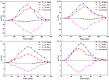
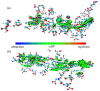
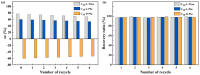
Three chiral nanorods of C14-l-Thea, C14-l-Phe, and C14-d-Phe were first synthesized and utilized as heterogeneous nucleants to enhance the resolution of racemic Asp via direct crystallization. Through the statistical analysis from 320 batches of nucleation experiments, we found that the apparent appearance diversity of two enantiomeric crystals of Asp existed in 80 homogeneous experiments without chiral nanorods. However, in 240 heterogeneous experiments with 4.0 wt % chiral nanorods of solute mass added, the appearance of those nuclei with the same chirality as the nanorods was apparently promoted, and that with the opposite chirality was totally inhibited. Under a supersaturation level of 1.08, the maximum ee of the initial nuclei was as high as 23.51%. When the cooling rate was 0.025 K/min, the ee of the product was up to 76.85% with a yield of 14.41%. Furthermore, the simulation results from quantum mechanics (QM) and molecular dynamics (MD) revealed that the higher chiral recognition ability of C14-l-Thea compared to C14-l-Phe that originated from the interaction difference between C14-l-Thea and Asp enantiomers was larger than that between C14-l-Phe and Asp enantiomers. Moreover, the constructed nanorods exhibited good stability and recyclability.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
[CuII(l-Phe)2-H]+ Complex: A Versatile Selector for Wide Enantiomeric Excess Determination and Chiral Recognition in Complicated Matrices by Post-column Infusion LC-Energy-resolved MS/MS.Anal Chem. 2025 Feb 18;97(6):3458-3468. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c05733. Epub 2025 Feb 8. Anal Chem. 2025. PMID: 39921622
-
Chiral carbon quantum dots as fluorescent probe for rapid chiral recognition of isoleucine enantiomers.Anal Chim Acta. 2021 Nov 1;1184:339012. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2021.339012. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Anal Chim Acta. 2021. PMID: 34625245
-
Mechanism of preferential enrichment, an unusual enantiomeric resolution phenomenon caused by polymorphic transition during crystallization of mixed crystals composed of two enantiomers.J Am Chem Soc. 2002 Nov 6;124(44):13139-53. doi: 10.1021/ja020454r. J Am Chem Soc. 2002. PMID: 12405843
-
Applications of ultrasound to chiral crystallization, resolution and deracemization.Ultrason Sonochem. 2018 May;43:184-192. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2018.01.014. Epub 2018 Jan 11. Ultrason Sonochem. 2018. PMID: 29555274 Review.
-
Nanophotonic Platforms for Chiral Sensing and Separation.Acc Chem Res. 2020 Mar 17;53(3):588-598. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00460. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Acc Chem Res. 2020. PMID: 31913015 Review.
Cited by
-
Sequential Amplification of Amino Acid Enantiomeric Excess by Conglomerate and Racemic Compound: Plausible Prebiotic Route Towards Homochirality.Orig Life Evol Biosph. 2023 Dec;53(3-4):175-185. doi: 10.1007/s11084-023-09642-1. Epub 2023 Oct 13. Orig Life Evol Biosph. 2023. PMID: 37831272
References
-
- Yang H.; Zheng W. H. Recent advances on nonenzymatic catalytic kinetic resolution of diols. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 583–591. 10.1016/j.tetlet.2017.12.080. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

