Morphological and Physiological Characteristics of Ruptured Plaques in Native Arteries and Neoatherosclerotic Segments: An OCT-Based and Computational Fluid Dynamics Study
- PMID: 35722127
- PMCID: PMC9204481
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.890799
Morphological and Physiological Characteristics of Ruptured Plaques in Native Arteries and Neoatherosclerotic Segments: An OCT-Based and Computational Fluid Dynamics Study
Abstract
Background: Intravascular imaging has been used to assess the morphology of lesions causing an acute coronary syndrome (ACS) in native vessels (NV) and identify differences between plaques that ruptured (PR) and caused an event and those that ruptured without clinical manifestations. However, there is no data about the morphological and physiological characteristics of neoatherosclerotic plaques that ruptured (PR-NA) which constitute a common cause of stent failure.
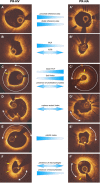
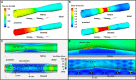
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed data from patients admitted with an acute myocardial infarction that had optical coherence tomography (OCT) imaging of the culprit vessel before balloon pre-dilation. OCT pullbacks showing PR were segmented at every 0.4 mm. The extent of the formed cavity, lipid and calcific tissue, thrombus, and macrophages were measured, and the fibrous cap thickness (FCT) and the incidence of micro-channels and cholesterol crystals were reported. These data were used to reconstruct a representative model of the native and neoatherosclerotic lesion geometry that was processed with computational fluid dynamics (CFD) techniques to estimate the distribution of the endothelial shear stress and plaque structural stress.
Result: Eighty patients were included in the present analysis: 56 had PR in NV (PR-NV group) and 24 in NA segments (PR-NA group). The PR-NV group had a larger minimum lumen area (2.93 ± 2.03 vs. 2.00 ± 1.26 mm2, p = 0.015) but similar lesion length and area stenosis compared to PR-NA group. The mean FCT (186 ± 65 vs. 232 ± 80 μm, p = 0.009) and the lipid index was smaller (16.7 ± 13.8 vs. 25.9 ± 14.1, p = 0.008) while the of calcific index (8.3 ± 9.5 vs. 2.2 ± 1.6%, p = 0.002) and the incidence of micro-channels (41.4 vs. 12.5%, p = 0.013) was higher in the PR-NV group. Conversely, there was no difference in the incidence of cholesterol crystals, thrombus burden or the location of the rupture site between groups. CFD analysis revealed higher maximum endothelial shear stress (19.1 vs. 11.0 Pa) and lower maximum plaque structural stress (38.8 vs. 95.1 kPa) in the PR-NA compared to the PR-NV model.
Conclusion: We reported significant morphological and physiological differences between culprit ruptured plaques in native and stented segments. Further research is needed to better understand the causes of these differences and the mechanisms regulating neoatherosclerotic lesion destabilization.
Keywords: computational fluid dynamics (CFD); endothelial shear stress; neoatherosclerosis; optical coherence tomography; plaque rupture; plaque structural stress.
Copyright © 2022 Jin, Torii, Ramasamy, Tufaro, Little, Konstantinou, Tan, Yap, Cooper, Crake, O’Mahony, Rakhit, Egred, Ahmed, Karamasis, Räber, Baumbach, Mathur and Bourantas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Fox KA, Clayton TC, Damman P, Pocock SJ, de Winter RJ, Tijssen JG, et al. Long-term outcome of a routine versus selective invasive strategy in patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome a meta-analysis of individual patient data. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2010) 55:2435–45. 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.03.007 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Joner M, Koppara T, Byrne RA, Castellanos MI, Lewerich J, Novotny J, et al. Neoatherosclerosis in patients with coronary stent thrombosis: findings from optical coherence tomography imaging (A Report of the PRESTIGE Consortium). JACC Cardiovasc Interv. (2018) 11:1340–50. 10.1016/j.jcin.2018.02.029 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

