Community mobility in the European regions during COVID-19 pandemic: A partitioning around medoids with noise cluster based on space-time autoregressive models
- PMID: 35722170
- PMCID: PMC9193889
- DOI: 10.1016/j.spasta.2021.100531
Community mobility in the European regions during COVID-19 pandemic: A partitioning around medoids with noise cluster based on space-time autoregressive models
Abstract
In this paper we propose a robust fuzzy clustering model, the STAR-based Fuzzy C-Medoids Clustering model with Noise Cluster, to define territorial partitions of the European regions (NUTS2) according to the workplaces mobility trends for places of work provided by Google with reference to the whole COVID-19 pandemic period. The clustering model takes into account both temporal and spatial information by means of the autoregressive temporal and spatial coefficients of the STAR model. The proposed clustering model through the noise cluster is capable of neutralizing the negative effects of noisy data. The main empirical results regard the expected direct relationship between the Community mobility trend and the lockdown periods, and a clear spatial interaction effect among neighboring regions.
Keywords: COVID-19 outbreak; Fuzzy C-medoids clustering; Google COVID-19 community mobility report; NUTS 2; Robust clustering; STAR model.
© 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

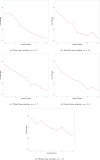



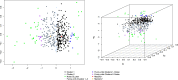
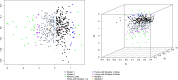



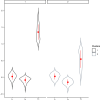
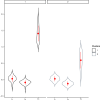

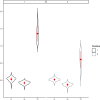






References
-
- Anon . 2021. Google COVID-19 community mobility reports. Retrieved from: https://www.google.com/covid19/mobility/april2021.
-
- Anselin L. Kluwer Academic; Dordrecht: 1988. Spatial Econometrics: Methods and Models.
-
- Bezdek J. Kluwer Academic; Norwell, MA, USA: 1981. Pattern Recognition with Fuzzy Objective Function Algorithms.
-
- Campello R.J.G.B., Hruschka E.R. A fuzzy extension of the silhouette width criterion for cluster analysis. Fuzzy Sets and Systems. 2006;157:2858–2875.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
