Human Virus Genomes Are Enriched in Conserved Adenine/Thymine/Uracil Multiple Tracts That Pause Polymerase Progression
- PMID: 35722311
- PMCID: PMC9198555
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.915069
Human Virus Genomes Are Enriched in Conserved Adenine/Thymine/Uracil Multiple Tracts That Pause Polymerase Progression
Abstract
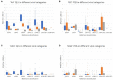
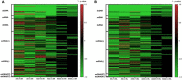
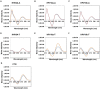
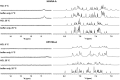
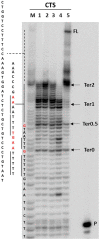
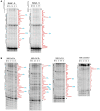
The DNA secondary structures that deviate from the classic Watson and Crick base pairing are increasingly being reported to form transiently in the cell and regulate specific cellular mechanisms. Human viruses are cell parasites that have evolved mechanisms shared with the host cell to support their own replication and spreading. Contrary to human host cells, viruses display a diverse array of nucleic acid types, which include DNA or RNA in single-stranded or double-stranded conformations. This heterogeneity improves the possible occurrence of non-canonical nucleic acid structures. We have previously shown that human virus genomes are enriched in G-rich sequences that fold in four-stranded nucleic acid secondary structures, the G-quadruplexes.Here, by extensive bioinformatics analysis on all available genomes, we showed that human viruses are enriched in highly conserved multiple A (and T or U) tracts, with such an array that they could in principle form quadruplex structures. By circular dichroism, NMR, and Taq polymerase stop assays, we proved that, while A/T/U-quadruplexes do not form, these tracts still display biological significance, as they invariably trigger polymerase pausing within two bases from the A/T/U tract. "A" bases display the strongest effect. Most of the identified A-tracts are in the coding strand, both at the DNA and RNA levels, suggesting their possible relevance during viral translation. This study expands on the presence and mechanism of nucleic acid secondary structures in human viruses and provides a new direction for antiviral research.
Keywords: adenines; conservation; non-canonical structures; polymerase progression; viruses.
Copyright © 2022 Ruggiero, Lavezzo, Grazioli, Zanin, Marušič, Plavec, Richter and Toppo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Conserved G-Quadruplexes Regulate the Immediate Early Promoters of Human Alphaherpesviruses.Molecules. 2019 Jun 27;24(13):2375. doi: 10.3390/molecules24132375. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31252527 Free PMC article.
-
A triple stranded G-quadruplex formation in the promoter region of human myosin β(Myh7) gene.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2018 Aug;36(11):2773-2786. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2017.1374211. Epub 2017 Sep 19. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2018. PMID: 28927343
-
Stable and Conserved G-Quadruplexes in the Long Terminal Repeat Promoter of Retroviruses.ACS Infect Dis. 2019 Jul 12;5(7):1150-1159. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.9b00011. Epub 2019 May 22. ACS Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31081611 Free PMC article.
-
Watson-Crick versus Hoogsteen Base Pairs: Chemical Strategy to Encode and Express Genetic Information in Life.Acc Chem Res. 2021 May 4;54(9):2110-2120. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00734. Epub 2021 Feb 16. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 33591181 Review.
-
The diverse structural landscape of quadruplexes.FEBS Lett. 2019 Aug;593(16):2083-2102. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13547. Epub 2019 Jul 30. FEBS Lett. 2019. PMID: 31325371 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

