Electroacupuncture of the Baihui and Shenting acupoints for vascular dementia in rats through the miR-81/IL-16/PSD-95 pathway
- PMID: 35722406
- PMCID: PMC9201176
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-22-2068
Electroacupuncture of the Baihui and Shenting acupoints for vascular dementia in rats through the miR-81/IL-16/PSD-95 pathway
Abstract
Background: There is currently no effective treatment for vascular dementia (VaD). Scalp electroacupuncture (EA) has served clinically as an alternative treatment for VaD, but its mechanism is still unclear. In this study, we investigated the effect of EA at the Baihui (GV 20) and Shenting (GV 24) acupoints on spatial learning and memory ability, and the expression level of microRNA-81 (miR-81), interleukin-16 (IL-16), and postsynaptic density protein-95 (PSD-95) in the frontal cortex of VaD rats.
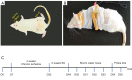
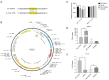
Methods: Male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into four groups, sham, VaD, non-acupuncture (non-AP) and EA group. The VaD model was established by permanent bilateral occlusion of the common carotid arteries. Morris Water Maze was used to assess the rats' spatial learning and memory. Immunochemistry (IHC), quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), and western blot analysis were performed to detect the expression level of miR-81, IL-16, and PSD-95. Finally, luciferase assay was used to determine the effect of miR-81 on IL-16 expression in PC12 cells.
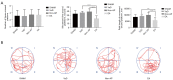
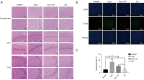
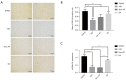
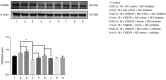
Results: The space exploration experiment of MWM showed the time and distance of the rat's activities around the platform were decreased in the EA group. Compared to the VaD and non-AP group, the number of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUDP nick-end labeling (TUNEL)-positive frontal cortical neurons was significantly decreased in EA group. The number of the PSD-95-positive cells and the miR-81 expression level in the frontal cortical in the EA group was dramatically increased in comparison with the other groups. In the PC12 cell validation experiment, IL-16 expression level was reduced under the condition of the miR-81 mimic treatment, while increased in the miR-81 inhibitor group. The PSD-95 protein level was up-regulated in the small interfering (si)RNA-IL16 group compared to the NC-IL16 groups with or without oxygen/glucose deprivation/reperfusion (OGD/R) conditions (P<0.05). However, this was abolished by miR-81 mimic.
Conclusions: In VaD rats, EA may improve spatial learning and memory through miR-81/IL-16/PSD-95 pathway.
Keywords: Baihui acupoint (GV 20); Shenting acupoint (GV 24); electroacupuncture (EA); miR-81; vascular dementia (VaD).
2022 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-22-2068/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Wang XX, Zhang B, Xia R, et al. Inflammation, apoptosis and autophagy as critical players in vascular dementia. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2020;24:9601-14. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
