Circ_UBE2D2 Attenuates the Progression of Septic Acute Kidney Injury in Rats by Targeting miR-370-3p/NR4A3 Axis
- PMID: 35722711
- PMCID: PMC9628902
- DOI: 10.4014/jmb.2112.12038
Circ_UBE2D2 Attenuates the Progression of Septic Acute Kidney Injury in Rats by Targeting miR-370-3p/NR4A3 Axis
Abstract
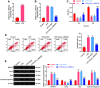
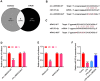
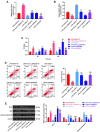
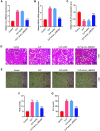
As circ_UBE2D2 has been confirmed to have targeted binding sites with multiple miRNAs involved in septic acute kidney injury (SAKI), efforts in this study are directed to unveiling the specific role and relevant mechanism of circ_UBE2D2 in SAKI. HK-2 cells were treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to construct SAKI model in vitro. After sh-circ_UBE2D2 was transfected into cells, the transfection efficiency was detected by qRT-PCR, cell viability and apoptosis were determined by MTT assay and flow cytometry, and expressions of Bcl-2, Bax and Cleaved-caspase 3 were quantified by western blot. Target genes associated with circ_UBE2D2 were predicted using bioinformatics analysis. After the establishment of SAKI rat model, HE staining and TUNEL staining were exploited to observe the effect of circ_UBE2D2 on tissue damage and cell apoptosis. The expression of circ_UBE2D2 was overtly elevated in LPS-induced HK-2 cells. Sh-circ_UBE2D2 can offset the inhibition of cell viability and the promotion of cell apoptosis induced by LPS. Circ_UBE2D2 and miR-370-3p as well as miR-370-3p and NR4A3 have targeted binding sites. MiR-370-3p inhibitor reversed the promoting effect of circ_UB2D2 silencing on viability of LPS-treated cells, but shNR4A3 neutralized the above inhibitory effect of miR-370-3p inhibitor. MiR-370-3p inhibitor weakened the down-regulation of NR4A3, Bax and Cleaved caspase-3 and the up-regulation of Bcl-2 induced by circ_UB2D2 silencing, but these trends were reversed by shNR4A3. In addition, sh-circ_UBE2D2 could alleviate the damage of rat kidney tissue. Circ_UBE2D2 mitigates the progression of SAKI in rats by targeting miR-370-3p/NR4A3 axis.
Keywords: Circ_UBE2D2; MiR-370-3p; NR4A3; apoptosis; septic acute kidney injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circ_0114427 promotes LPS-induced septic acute kidney injury by modulating miR-495-3p/TRAF6 through the NF-κB pathway.Autoimmunity. 2022 Feb;55(1):52-64. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2021.1995861. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Autoimmunity. 2022. PMID: 34730059
-
Circular RNA-UBE2D2 accelerates the proliferation and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer cells via modulating microRNA-376a-3p/Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 4γ2 axis.Bioengineered. 2022 Mar;13(3):5942-5953. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2027068. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35196197 Free PMC article.
-
Circ_0114428 Regulates Sepsis-Induced Kidney Injury by Targeting the miR-495-3p/CRBN Axis.Inflammation. 2021 Aug;44(4):1464-1477. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01432-z. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Inflammation. 2021. PMID: 33830389
-
Research progress on miR-124-3p in the field of kidney disease.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Aug 7;25(1):252. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03688-7. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39112935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Response of Macrophages in Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury.J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 31;12(3):1101. doi: 10.3390/jcm12031101. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36769749 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Knockdown of circ-Gatad1 alleviates LPS induced HK2 cell injury via targeting miR-22-3p/TRPM7 axis in septic acute kidney.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Mar 5;25(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03513-1. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38443846 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of semen cuscutae flavonoid on Sertoli cells and blood-testis barrier in male infertility: integrating network pharmacology and experimental verification.Pharm Biol. 2023 Dec;61(1):986-999. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2023.2229380. Pharm Biol. 2023. PMID: 37386769 Free PMC article.
-
Kidney Injury: Focus on Molecular Signaling Pathways.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(28):4510-4533. doi: 10.2174/0109298673271547231108060805. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38314680 Review.
-
Cuproptosis-related Gene Signatures and Immunological Characterization in Sepsis-associated Acute Lung Injury.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025;28(7):1205-1219. doi: 10.2174/0113862073290692240509094709. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025. PMID: 38779731 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

