Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 expression and immunotherapy efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 35722982
- PMCID: PMC9459341
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.15464
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 expression and immunotherapy efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
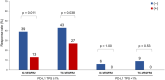
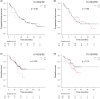
It is unclear whether tumor vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 expression affects the therapeutic efficacy of immune-checkpoint inhibitors and antiangiogenic agents. This retrospective, multicenter study included patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer who were treated with immune-checkpoint inhibitors. We constructed tissue microarrays and performed immunohistochemistry with an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 antibody. We analyzed immune and tumor cell staining separately in order to determine their correlation with the objective response rate, progression-free survival, and overall survival in patients receiving immune-checkpoint inhibitors. Of 364 patients, 37 (10%) expressed vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 in immune cells and 165 (45%) in tumor cells. The objective response rate, progression-free survival, and overall survival were significantly worse in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy who expressed vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 in immune cells than those who did not (10% vs 30%, p = 0.028; median = 2.2 vs 3.6 months, p = 0.012; median = 7.9 vs 17.0 months, p = 0.049, respectively), while there was no significant difference based on tumor cell expression (24% vs 30%, p = 0.33; median = 3.1 vs 3.5 months, p = 0.55; median = 13.6 vs 16.8 months, p = 0.31). There was no significant difference in overall survival between patients treated with and without antiangiogenic agents in any treatment period based on vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 expression. Immune checkpoint inhibitor efficacy was limited in patients expressing vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 in immune cells.
Keywords: immune checkpoint inhibitor; lung cancer; programmed death-ligand 1; tissue microarray; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.
© 2022 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures



References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;8(6):394‐424. - PubMed
-
- Reck M, Rodriguez‐Abreu D, Robinson AG, et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD‐L1‐positive non‐small‐cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(19):1823‐1833. - PubMed
-
- Herbst RS, Giaccone G, de Marinis F, et al. Atezolizumab for first‐line treatment of PD‐L1‐selected patients with NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(14):1328‐1339. - PubMed
-
- Hellmann MD, Paz‐Ares L, Bernabe Caro R, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced non‐small‐cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(21):2020‐2031. - PubMed
-
- Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J, et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR‐mutated advanced non‐small‐cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(2):113‐125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

