Probing Neuropeptide Volume Transmission In Vivo by Simultaneous Near-Infrared Light-Triggered Release and Optical Sensing
- PMID: 35723610
- PMCID: PMC9388559
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202206122
Probing Neuropeptide Volume Transmission In Vivo by Simultaneous Near-Infrared Light-Triggered Release and Optical Sensing
Abstract
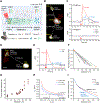
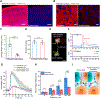
Neuropeptides are abundant signaling molecules in the central nervous system. Yet remarkably little is known about their spatiotemporal spread and biological activity. Here, we developed an integrated optical approach using Plasmonic nAnovesicles and cell-based neurotransmitter fluorescent engineered reporter (CNiFER), or PACE, to probe neuropeptide signaling in the mouse neocortex. Small volumes (fL to pL) of exogenously supplied somatostatin-14 (SST) can be rapidly released under near-infrared light stimulation from nanovesicles implanted in the brain and detected by SST2 CNiFERs with nM sensitivity. Our measurements reveal reduced but synchronized SST transmission within 130 μm, and markedly smaller and delayed transmission at longer distances. These measurements enabled a quantitative estimation of the SST loss rate due to peptide degradation and binding. PACE offers a new tool for determining the spatiotemporal scales of neuropeptide volume transmission and signaling in the brain.
Keywords: Biosensors; Brain; Neuropeptide Release; Neuropeptide Transmission; Plasmonic Nanovesicles.
© 2022 Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Lacin E, Muller A, Fernando M, Kleinfeld D, Slesinger PA, J. Vis. Exp 2016, e53290; - PMC - PubMed
- Muller A, Joseph V, Slesinger PA, Kleinfeld D, Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 1245–1252; - PMC - PubMed
- Foo C, Lozada A, Aljadeff J, Li Y, Wang JW, Slesinger PA, Kleinfeld D, Curr. Biol 2021, 31, 4111–4119. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

