The diagnostic importance of periostin as a biomarker in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp
- PMID: 35723731
- PMCID: PMC9207425
- DOI: 10.1007/s00405-022-07492-7
The diagnostic importance of periostin as a biomarker in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp
Abstract
Purpose: The current studies in the literature report that periostin contributes to the formation of nasal polyps and may be a molecular biomarker for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP). This study aims to investigate the effect of periostin in determining polyp burden in CRSwNP patients and evaluate its impact on postoperative surgical results and its functionality as a biomarker.
Methods: The study included 26 patients who underwent endoscopic sinus surgery due to CRSwNP and 30 patients who were scheduled to undergo septoplasty due to isolated nasal septum deviation. We performed preoperative Lund-Mackay scoring and preoperative and postoperative SNOT-22 and Modified Lund-Kennedy scoring for the patients. Tissue and serum samples were collected from all patients in surgery and another serum sample was taken from CRSwNP patients at postoperative month 6.
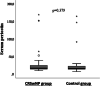
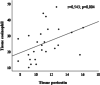
Results: Tissue eosinophil (p < 0.001), preoperative serum (p < 0.001), and tissue (p = 0.002) periostin were significantly higher in the CRSwNP group. We observed a statistically significant positive correlation between tissue eosinophil values and tissue periostin values in CRSwNP patients (p = 0.004). We found a statistically significant positive correlation between the tissue periostin values and postoperative SNOT-22 scores of the CRSwNP group patients (p = 0.005).
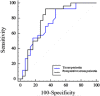
Conclusion: According to the results of our study, we think that periostin can be used as a biomarker in the prediction, determination of disease severity, and prognosis of CRSwNP. Comprehensive cohort studies with larger patient series are needed to provide more information on the role and effects of periostin in cases of CRSwNP undergoing surgical treatment.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Nasal polyps; Nasal surgical procedure; Periostin; Sinusitis.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no declarations of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

