A dual-target herbicidal inhibitor of lysine biosynthesis
- PMID: 35723913
- PMCID: PMC9208756
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.78235
A dual-target herbicidal inhibitor of lysine biosynthesis
Abstract
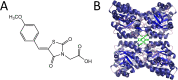
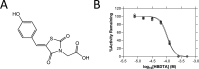
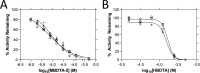
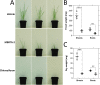
Herbicides with novel modes of action are urgently needed to safeguard global agricultural industries against the damaging effects of herbicide-resistant weeds. We recently developed the first herbicidal inhibitors of lysine biosynthesis, which provided proof-of-concept for a promising novel herbicide target. In this study, we expanded upon our understanding of the mode of action of herbicidal lysine biosynthesis inhibitors. We previously postulated that these inhibitors may act as proherbicides. Here, we show this is not the case. We report an additional mode of action of these inhibitors, through their inhibition of a second lysine biosynthesis enzyme, and investigate the molecular determinants of inhibition. Furthermore, we extend our herbicidal activity analyses to include a weed species of global significance.
Keywords: A. thaliana; biochemistry; chemical biology; diaminopimelate pathway; herbicide; lysine; plant biology; weeds.
© 2022, Mackie et al.
Conflict of interest statement
EM, AB, RC, AG No competing interests declared, BA B.M.A. are listed as inventors on a patent pertaining to inhibitors described in the manuscript. Patent Title: Heterocyclic inhibitors of lysine biosynthesis via the diaminopimelate pathway; International patent (PCT) No.: WO2018187845A1; Granted: 18/10/2018, TS T.P.S.C. is listed as inventors on a patent pertaining to inhibitors described in the manuscript. Patent Title: Heterocyclic inhibitors of lysine biosynthesis via the diaminopimelate pathway; International patent (PCT) No.: WO2018187845A1; Granted: 18/10/2018
Figures

References
-
- Busi R, Beckie HJ. Are herbicide mixtures unaffected by resistance? A case study with Lolium rigidum. Weed Research. 2020;61:92–99. doi: 10.1111/wre.12453. - DOI
-
- Christoff RM, Costa TP, Bayat S, Holien JK, Perugini MA, Abbott BM. Synthesis and structure-activity relationship studies of 2,4-thiazolidinediones and analogous heterocycles as inhibitors of dihydrodipicolinate synthase. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 2021;52:116518. doi: 10.1016/J.BMC.2021.116518. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dayer P, Desmeules J, Leemann T, Striberni R. Bioactivation of the narcotic drug codeine in human liver is mediated by the polymorphic monooxygenase catalyzing debrisoquine 4-hydroxylation (cytochrome P-450 dbl/bufI. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 1988;152:411–416. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80729-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

