Comparative analysis of machine learning algorithms on the microbial strain-specific AMP prediction
- PMID: 35724561
- PMCID: PMC9294419
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbac233
Comparative analysis of machine learning algorithms on the microbial strain-specific AMP prediction
Abstract
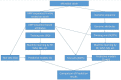
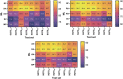
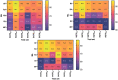
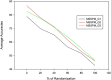
The evolution of drug-resistant pathogenic microbial species is a major global health concern. Naturally occurring, antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are considered promising candidates to address antibiotic resistance problems. A variety of computational methods have been developed to accurately predict AMPs. The majority of such methods are not microbial strain specific (MSS): they can predict whether a given peptide is active against some microbe, but cannot accurately calculate whether such peptide would be active against a particular MS. Due to insufficient data on most MS, only a few MSS predictive models have been developed so far. To overcome this problem, we developed a novel approach that allows to improve MSS predictive models (MSSPM), based on properties, computed for AMP sequences and characteristics of genomes, computed for target MS. New models can perform predictions of AMPs for MS that do not have data on peptides tested on them. We tested various types of feature engineering as well as different machine learning (ML) algorithms to compare the predictive abilities of resulting models. Among the ML algorithms, Random Forest and AdaBoost performed best. By using genome characteristics as additional features, the performance for all models increased relative to models relying on AMP sequence-based properties only. Our novel MSS AMP predictor is freely accessible as part of DBAASP database resource at http://dbaasp.org/prediction/genome.
Keywords: AMP prediction; antimicrobial peptides; machine learning.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Pinacho-Castellanos SA, García-Jacas CR, Gilson MK, et al. Alignment-free antimicrobial peptide predictors: improving performance by a thorough analysis of the largest available data set. J Chem Inf Model 2021;61:3141–57. - PubMed
-
- Kavousi K, Bagheri M, Behrouzi S, et al. IAMPE: NMR assisted computational prediction of antimicrobial peptides. J Chem Inf Model 2020;60:4691–701. - PubMed
-
- Akbar S, Hayat AA, , et al. iAtbP-Hyb-EnC: prediction of antitubercular peptides via heterogeneous feature representation and genetic algorithm based ensemble learning model. Comput Biol Med 2021;137:104778. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

