Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System in Women Using Combined Oral Contraceptive: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 35724684
- PMCID: PMC9948294
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0042-1745790
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System in Women Using Combined Oral Contraceptive: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Objective: To describe the effects of combined oral contraceptives (COC) on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS).
Data sources: This is a systematic review according to the criteria of Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA), registered in PROSPERO under the ID: CRD42020200019. Searches were performed between August 2020 and December 2021, in the following databases: Medline via Pubmed, Cochrane Central Library, Scientific Electronic Library Online, and Latin American and Caribbean Literature in Health Sciences via Virtual Health Library. The effects of the combined oral contraceptive on plasma renin activity values, plasma renin values, angiotensinogen values- also known as plasma renin substrate- angiotensin, and/or aldosterone values.
Study selection: A total of 877 studies were selected and, of these, 10 articles met the eligibility criteria and were included in this review.
Data collection: Data were combined through qualitative synthesis and included in a spreadsheet previously prepared by the authors.
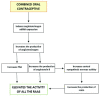
Data synthesis: The collected samples ranged from 18 to 137 participants, totaling 501 women aged between 18 and 49 years throughout all studies. The studies showed increased activity of plasma renin, plasma renin substrate, angiotensin II, and aldosterone in this population.
Conclusion: The findings of this study suggest that the COC promotes greater activation of the RAAS. Supporting the idea that its use is related to an increased risk of cardiovascular events, including systemic arterial hypertension.
Objetivo: Descrever os efeitos do contraceptivo oral combinado (COC) no sistema renina-angiotensina-aldosterona (SRAA).
Fontes dos dados: Trata-se de uma revisão sistemática de acordo com os critérios do Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA), registrada no PROSPERO sob ID: CRD42020200019. As buscas foram realizadas entre agosto de 2020 e dezembro de 2021 nas bases de dados: Medline via Pubmed, Biblioteca Cochrane Central, Scientific Electronic Library Online, e Literatura Latino-americana e do Caribe em Ciências da Saúde via Biblioteca Virtual em Saúde. Consultado os artigos sobre os efeitos do contraceptivo oral combinado nos valores da atividade da renina plasmática, valores plasmáticos da renina, valores do angiotensinogênio – também conhecido como substrato da renina plasmática –, valores da angiotensina e/ou aldosterona. SELEçãO DOS ESTUDOS: Foram selecionados 877 estudos e, destes, 10 artigos preencheram os critérios de elegibilidade e foram incluídos nesta revisão.
Coleta de dados: Os dados foram combinados por meio de síntese qualitativa e inclusos em uma planilha elaborada previamente pelos autores. SíNTESE DOS DADOS: As amostras coletadas variavam entre 18 e 137 participantes, totalizando 501 mulheres com idade entre 18 e 49 anos em todos os estudos. Os estudos apresentaram aumento da atividade da renina plasmática, do substrato da renina plasmática, da angiotensina II e da aldosterona nessa população. CONCLUSãO: Os achados deste estudo sugerem que o COC promove maior ativação do SRAA. Apoiando a ideia de que o seu uso esteja relacionado ao aumento do risco de eventos cardiovasculares, incluindo a hipertensão arterial sistêmica.
Federação Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, permitting unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction so long as the original work is properly cited. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous