Sorting through the extensive and confusing roles of sortilin in metabolic disease
- PMID: 35724703
- PMCID: PMC9356209
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jlr.2022.100243
Sorting through the extensive and confusing roles of sortilin in metabolic disease
Abstract
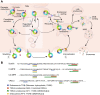
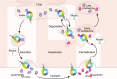
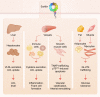
Sortilin is a post-Golgi trafficking receptor homologous to the yeast vacuolar protein sorting receptor 10 (VPS10). The VPS10 motif on sortilin is a 10-bladed β-propeller structure capable of binding more than 50 proteins, covering a wide range of biological functions including lipid and lipoprotein metabolism, neuronal growth and death, inflammation, and lysosomal degradation. Sortilin has a complex cellular trafficking itinerary, where it functions as a receptor in the trans-Golgi network, endosomes, secretory vesicles, multivesicular bodies, and at the cell surface. In addition, sortilin is associated with hypercholesterolemia, Alzheimer's disease, prion diseases, Parkinson's disease, and inflammation syndromes. The 1p13.3 locus containing SORT1, the gene encoding sortilin, carries the strongest association with LDL-C of all loci in human genome-wide association studies. However, the mechanism by which sortilin influences LDL-C is unclear. Here, we review the role sortilin plays in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases and describe in detail the large and often contradictory literature on the role of sortilin in the regulation of LDL-C levels.
Keywords: CVD; LDL/metabolism; SORT1; VPS10; cellular trafficking; cholesterol/metabolism; cholesterol/trafficking; dyslipidemias; lipoproteins/metabolism; sortilin.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Petersen C.M., Nielsen M.S., Nykjaer A., Jacobsen L., Tommerup N., Rasmussen H.H., et al. Molecular identification of a novel candidate sorting receptor purified from human brain by receptor-associated protein affinity chromatography. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272(6):3599–3605. - PubMed
-
- Sarti M., Farquhar M.G., Orlando R.A. The receptor-associated protein (RAP) interacts with several resident proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum including a glycoprotein related to actin. Exp. Cell Res. 2000;260(2):199–207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

