Foundational biodiversity effects propagate through coastal food webs via multiple pathways
- PMID: 35724974
- PMCID: PMC9787374
- DOI: 10.1002/ecy.3796
Foundational biodiversity effects propagate through coastal food webs via multiple pathways
Abstract
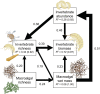
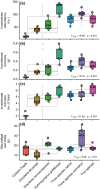
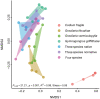
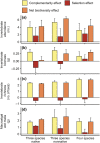
Relatively few studies have attempted to resolve the pathways through which the effects of biodiversity on ecosystem functioning cascade from one trophic level to another. Here, we manipulated the richness of habitat-forming seaweeds in a western Atlantic estuary to explore how changes in foundation species diversity affect the structure and functioning of the benthic consumer communities that they support. Structural equation modeling revealed that macroalgal richness enhanced invertebrate abundance, biomass, and diversity, both directly by changing the quality and palatability of the foundational substrate and indirectly by increasing the total biomass of available habitat. Consumer responses were largely driven by a single foundational seaweed, although stronger complementarity among macroalgae was observed for invertebrate richness. These findings with diverse foundational phyla extend earlier inferences from terrestrial grasslands by showing that biodiversity effects can simultaneously propagate through multiple independent pathways to maintain animal foodwebs. Our work also highlights the potential ramifications of human-induced changes in marine ecosystems.
Keywords: biodiversity-ecosystem functioning; coastal marine ecosystems; epifaunal invertebrates; foundation species; niche complementarity; nonnative species; plant diversity effects; structural equation modeling.
© 2022 The Authors. Ecology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Ecological Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Angelini, C. , Altieri A. H., Silliman B. R., and Bertness M. D.. 2011. “Interactions among Foundation Species and their Consequences for Community Organization, Biodiversity, and Conservation.” Bioscience 61: 782–9.
-
- Bates, C. R. , and DeWreede R. E.. 2007. “Do Changes in Seaweed Biodiversity Influence Associated Invertebrate Epifauna?” Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 344: 206–14.
-
- Bax, N. , Williamson A., Aguero M., Gonzalez E., and Geeves W.. 2003. “Marine Invasive Alien Species: A Threat to Global Biodiversity.” Marine Policy 27: 313–23.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
