Multimodal deep learning for Alzheimer's disease dementia assessment
- PMID: 35725739
- PMCID: PMC9209452
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-31037-5
Multimodal deep learning for Alzheimer's disease dementia assessment
Abstract
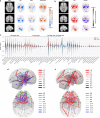
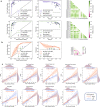
Worldwide, there are nearly 10 million new cases of dementia annually, of which Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common. New measures are needed to improve the diagnosis of individuals with cognitive impairment due to various etiologies. Here, we report a deep learning framework that accomplishes multiple diagnostic steps in successive fashion to identify persons with normal cognition (NC), mild cognitive impairment (MCI), AD, and non-AD dementias (nADD). We demonstrate a range of models capable of accepting flexible combinations of routinely collected clinical information, including demographics, medical history, neuropsychological testing, neuroimaging, and functional assessments. We then show that these frameworks compare favorably with the diagnostic accuracy of practicing neurologists and neuroradiologists. Lastly, we apply interpretability methods in computer vision to show that disease-specific patterns detected by our models track distinct patterns of degenerative changes throughout the brain and correspond closely with the presence of neuropathological lesions on autopsy. Our work demonstrates methodologies for validating computational predictions with established standards of medical diagnosis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
V.B.K. reports honoraria from invited scientific presentations to industry not exceeding $5000/year. He also serves as a consultant to Davos Alzheimer’s Collaborative. R.A. is a scientific advisor to Signant Health and consultant to Biogen. K.L.P. reports honoraria from invited scientific presentations to universities and professional societies not exceeding $5,000/year and has received consulting fees from Curasen. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AG054076/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG016495/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG065156/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066515/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG062109/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG072654/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS115114/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL159620/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG062109/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013846/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA253498/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 NS075097/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG068753/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066546/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG033040/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

