Adaptive stimulation of macropinocytosis overcomes aspartate limitation in cancer cells under hypoxia
- PMID: 35726024
- PMCID: PMC9678334
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-022-00583-z
Adaptive stimulation of macropinocytosis overcomes aspartate limitation in cancer cells under hypoxia
Abstract
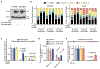
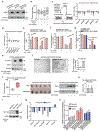
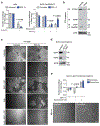
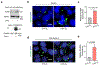
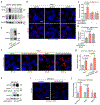
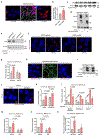
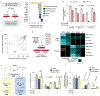
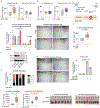
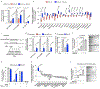
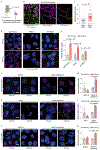
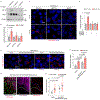
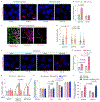
Stress-adaptive mechanisms enable tumour cells to overcome metabolic constraints under nutrient and oxygen shortage. Aspartate is an endogenous metabolic limitation under hypoxic conditions, but the nature of the adaptive mechanisms that contribute to aspartate availability and hypoxic tumour growth are poorly understood. Here we identify GOT2-catalysed mitochondrial aspartate synthesis as an essential metabolic dependency for the proliferation of pancreatic tumour cells under hypoxic culture conditions. In contrast, GOT2-catalysed aspartate synthesis is dispensable for pancreatic tumour formation in vivo. The dependence of pancreatic tumour cells on aspartate synthesis is bypassed in part by a hypoxia-induced potentiation of extracellular protein scavenging via macropinocytosis. This effect is mutant KRAS dependent, and is mediated by hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF1A) and its canonical target carbonic anhydrase-9 (CA9). Our findings reveal high plasticity of aspartate metabolism and define an adaptive regulatory role for macropinocytosis by which mutant KRAS tumours can overcome nutrient deprivation under hypoxic conditions.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
K.B. is scientific adviser to Nanocare Pharmaceuticals and a consultant to Barer Institute. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
GOT2 consider the tumor microenvironment.Trends Cancer. 2022 Nov;8(11):884-886. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2022.09.004. Epub 2022 Sep 21. Trends Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36153305 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DeBerardinis RJ, Lum JJ, Hatzivassiliou G & Thompson CB The biology of cancer: metabolic reprogramming fuels cell growth and proliferation. Cell Metab. 7, 11–20 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

