Analysis of lorlatinib analogs reveals a roadmap for targeting diverse compound resistance mutations in ALK-positive lung cancer
- PMID: 35726063
- PMCID: PMC9732888
- DOI: 10.1038/s43018-022-00399-6
Analysis of lorlatinib analogs reveals a roadmap for targeting diverse compound resistance mutations in ALK-positive lung cancer
Abstract
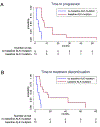
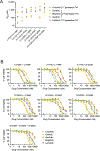
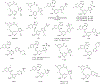
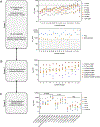
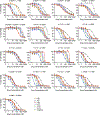
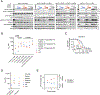
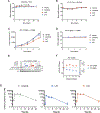
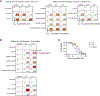
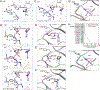
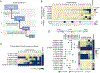
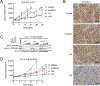
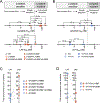
Lorlatinib is currently the most advanced, potent and selective anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer in the clinic; however, diverse compound ALK mutations driving therapy resistance emerge. Here, we determine the spectrum of lorlatinib-resistant compound ALK mutations in patients, following treatment with lorlatinib, the majority of which involve ALK G1202R or I1171N/S/T. We further identify structurally diverse lorlatinib analogs that harbor differential selective profiles against G1202R versus I1171N/S/T compound ALK mutations. Structural analysis revealed increased potency against compound mutations through improved inhibition of either G1202R or I1171N/S/T mutant kinases. Overall, we propose a classification of heterogenous ALK compound mutations enabling the development of distinct therapeutic strategies for precision targeting following sequential tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS STATEMENT
Figures




Comment in
-
Targeting drug-resistant mutations in ALK.Nat Cancer. 2022 Jun;3(6):659-661. doi: 10.1038/s43018-022-00390-1. Nat Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35726064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Soda M et al. , Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature 448, 561–566 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Solomon BJM, T.; Kim D; Wu Y; Nakagawa K; Mekhail T; Felip E; Cappuzzo F; Paolini J; Usari T; Iyer S; Reisman A; Wilner KD; Tursi J; Blackhall F, First-Line Crizotinib versus Chemotherapy in ALK-Positive Lung Cancer. N Engl J Med 373, 1582 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

