Isavuconazole plasma concentrations in critically ill patients during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
- PMID: 35726095
- PMCID: PMC9384295
- DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkac196
Isavuconazole plasma concentrations in critically ill patients during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
Abstract
Background: Isavuconazole is an antifungal drug used for treatment of invasive fungal infections. Critically ill COVID-19 and influenza patients require extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) in cases with severe acute respiratory distress syndrome and have risk factors for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Little is known about isavuconazole plasma concentrations during ECMO.
Objectives: To determine isavuconazole plasma concentrations in seven patients treated with intravenous isavuconazole under ECMO and the influence of the ECMO circuit immediately after the first isavuconazole dose.
Methods: Critically ill patients treated with isavuconazole (standard doses) and ECMO were included in this study. Sixty-four blood samples used for measurement of isavuconazole concentrations were collected at several timepoints starting 2 h after the first isavuconazole dose up to 168 h. An additional 27 blood samples were drawn from the inflow and outflow line of the membrane oxygenator to assess any potential isavuconazole clearance effect of the ECMO oxygenation device and the lines.
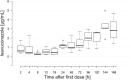
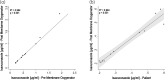
Results: Median isavuconazole trough levels above 1 μg/mL (min. 0.83, max. 1.73) or 2 μg/mL (min. 0.84, max. 2.97) were achieved 24 h or 96 h after the first dose of isavuconazole. The isavuconazole plasma concentrations pre (inflow line) and post (outflow line) the membrane oxygenator were directly correlated (ρ = 0.987, R2 = 0.994, P < 0.001). Post membrane oxygenator isavuconazole concentrations were directly correlated to contemporaneous samples obtained from the arterial lines of patients (ρ = 0.942, R2 = 0.945, P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Isavuconazole concentrations might be influenced by the higher volume of distribution due to ECMO therapy, but were not altered by the ECMO oxygenator and achieved median plasma concentrations >1 μg/mL 24 h after the first loading dose.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Comment in
-
Comment on: Isavuconazole plasma concentrations in critically ill patients during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2022 Nov 28;77(12):3526-3527. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkac316. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2022. PMID: 36124899 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cornely OA, Alastruey-Izquierdo A, Arenz D et al. Global guideline for the diagnosis and management of mucormycosis: an initiative of the European Confederation of Medical Mycology in cooperation with the Mycoses Study Group Education and Research Consortium. Lancet Infect Dis 2019; 19: e405–21. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schauwvlieghe A, Rijnders BJA, Philips N et al. Invasive aspergillosis in patients admitted to the intensive care unit with severe influenza: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Respir Med 2018; 6: 782–92. - PubMed

