Networks Underlie Temporal Onset of Dysplasia-Related Epilepsy: A MELD Study
- PMID: 35726354
- PMCID: PMC10410674
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.26442
Networks Underlie Temporal Onset of Dysplasia-Related Epilepsy: A MELD Study
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to evaluate if focal cortical dysplasia (FCD) co-localization to cortical functional networks is associated with the temporal distribution of epilepsy onset in FCD.
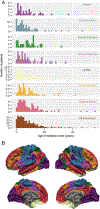
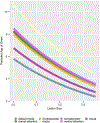
Methods: International (20 center), retrospective cohort from the Multi-Centre Epilepsy Lesion Detection (MELD) project. Patients included if >3 years old, had 3D pre-operative T1 magnetic resonance imaging (MRI; 1.5 or 3 T) with radiologic or histopathologic FCD after surgery. Images processed using the MELD protocol, masked with 3D regions-of-interest (ROI), and co-registered to fsaverage_sym (symmetric template). FCDs were then co-localized to 1 of 7 distributed functional cortical networks. Negative binomial regression evaluated effect of FCD size, network, histology, and sulcal depth on age of epilepsy onset. From this model, predictive age of epilepsy onset was calculated for each network.
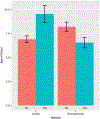
Results: Three hundred eighty-eight patients had median age seizure onset 5 years (interquartile range [IQR] = 3-11 years), median age at pre-operative scan 18 years (IQR = 11-28 years). FCDs co-localized to the following networks: limbic (90), default mode (87), somatomotor (65), front parietal control (52), ventral attention (32), dorsal attention (31), and visual (31). Larger lesions were associated with younger age of onset (p = 0.01); age of epilepsy onset was associated with dominant network (p = 0.04) but not sulcal depth or histology. Sensorimotor networks had youngest onset; the limbic network had oldest age of onset (p values <0.05).
Interpretation: FCD co-localization to distributed functional cortical networks is associated with age of epilepsy onset: sensory neural networks (somatomotor and visual) with earlier onset, and limbic latest onset. These variations may reflect developmental differences in synaptic/white matter maturation or network activation and may provide a biological basis for age-dependent epilepsy onset expression. ANN NEUROL 2022;92:503-511.
© 2022 American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest.
Figures
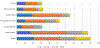
References
-
- Fauser S, Huppertz HJ, Bast T, et al. Clinical characteristics in focal cortical dysplasia: a retrospective evaluation in a series of 120 patients. Brain: J Neurol 2006. Jul;129:1907–1916. - PubMed
-
- Siegel AM, Cascino GD, Elger CE, et al. Adult-onset epilepsy in focal cortical dysplasia of Taylor type. Neurology 2005;64:1771–1774. - PubMed
-
- Racz A, Müller AM, Schwerdt J, et al. Age at epilepsy onset in patients with focal cortical dysplasias, gangliogliomas and dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumours. Seizure 2018. May;58:82–89. - PubMed
-
- Wiwattanadittakul N, Suwannachote S, You X, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution and age of seizure onset in a pediatric epilepsy surgery cohort with cortical dysplasia. Epilepsy Res 2021. Mar;2:106598. - PubMed
-
- Lortie A, Plouin P, Chiron C, et al. Characteristics of epilepsy in focal cortical dysplasia in infancy. Epilepsy Res 2002. Sep;51:133–145. - PubMed

