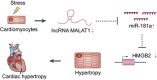
MALAT1 regulates hypertrophy of cardiomyocytes by modulating the miR-181a/HMGB2 pathway
- PMID: 35726535
- PMCID: PMC9251611
- DOI: 10.4081/ejh.2022.3426
MALAT1 regulates hypertrophy of cardiomyocytes by modulating the miR-181a/HMGB2 pathway
Abstract
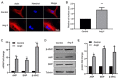
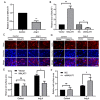
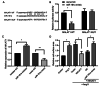
Noncoding RNAs are important for regulation of cardiac hypertrophy. The function of MALAT1 (a long noncoding mRNA), miR-181a, and HMGB2; their contribution to cardiac hypertrophy; and the regulatory relationship between them during this process remain unknown. In the present study, we treated primary cardiomyocytes with angiotensin II (Ang II) to mimic cardiac hypertrophy. MALAT1 expression was significantly downregulated in Ang II-treated cardiomyocytes compared with control cardiomyocytes. Ang II-induced cardiac hypertrophy was suppressed by overexpression of MALAT1 and promoted by genetic knockdown of MALAT1. A dual-luciferase reporter assay demonstrated that MALAT1 acted as a sponge for miR-181a and inhibited its expression during cardiac hypertrophy. Cardiac hypertrophy was suppressed by overexpression of a miR-181a inhibitor and enhanced by overexpression of a miR-181a mimic. HMGB2 was downregulated during cardiac hypertrophy and was identified as a target of miR-181a by bioinformatics analysis and a dual-luciferase reporter assay. miR-181a overexpression decreased the mRNA and protein levels of HMGB2. Rescue experiments indicated that MALAT1 overexpression reversed the effect of miR-181a on HMGB2 expression. In summary, the results of the present study show that MALAT1 acts as a sponge for miR-181a and thereby regulates expression of HMGB2 and development of cardiac hypertrophy. The novel MALAT1/miR-181a/HMGB2 axis might play a crucial role in cardiac hypertrophy and serve as a new therapeutic target.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Downregulation of lncRNA MALAT1 Inhibits Angiotensin II-induced Hypertrophic Effects of Cardiomyocytes by Regulating SIRT4 via miR-93-5p.Int Heart J. 2022;63(3):602-611. doi: 10.1536/ihj.21-332. Int Heart J. 2022. PMID: 35650160
-
Involvement of microRNA-23b-5p in the promotion of cardiac hypertrophy and dysfunction via the HMGB2 signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Aug;116:108977. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108977. Epub 2019 May 17. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31103821
-
MiR-181a mediates Ang II-induced myocardial hypertrophy by mediating autophagy.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017 Dec;21(23):5462-5470. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201712_13936. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29243791
-
LncRNA MALAT1/miR-181a-5p affects the proliferation and adhesion of myeloma cells via regulation of Hippo-YAP signaling pathway.Cell Cycle. 2019 Oct;18(19):2509-2523. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1652034. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Cell Cycle. 2019. PMID: 31397203 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of long non-coding RNA metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 attenuates high glucose-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis via regulation of miR-181a-5p.Exp Anim. 2020 Jan 29;69(1):34-44. doi: 10.1538/expanim.19-0058. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Exp Anim. 2020. PMID: 31353329 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Using Machine Learning Methods in Identifying Genes Associated with COVID-19 in Cardiomyocytes and Cardiac Vascular Endothelial Cells.Life (Basel). 2023 Apr 14;13(4):1011. doi: 10.3390/life13041011. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37109540 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction Between Malat1 and miR-499-5p Regulates Meis1 Expression and Function with a Net Impact on Cell Proliferation.Cells. 2025 Jan 16;14(2):125. doi: 10.3390/cells14020125. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39851553 Free PMC article.
-
An In-Depth Insight into Clinical, Cellular and Molecular Factors in COVID19-Associated Cardiovascular Ailments for Identifying Novel Disease Biomarkers, Drug Targets and Clinical Management Strategies.Arch Microbiol Immunol. 2024;8(3):290-308. doi: 10.26502/ami.936500177. Epub 2024 Jul 19. Arch Microbiol Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39703820 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding RNAs as Key Regulators for Cardiac Development and Cardiovascular Diseases.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023 Apr 12;10(4):166. doi: 10.3390/jcdd10040166. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023. PMID: 37103045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The regulatory activities of MALAT1 in the development of bone and cartilage diseases.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 14;13:1054827. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1054827. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36452326 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yurista SR, Chong CR, Badimon JJ, Kelly DP, de Boer RA, Westenbrink BD. Therapeutic potential of ketone bodies for patients with cardiovascular disease: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol 2021;77:1660-9. - PubMed
-
- Tada H, Fujino N, Hayashi K, Kawashiri MA, Takamura M. Human genetics and its impact on cardiovascular disease. J Cardiol 2022;79:233-9. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Xin L, Xiang M, Shang C, Wang Y, Wang Y, et al. . The molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and its role in cardiovascular disease. Biomed Pharmacother 2022;145:112423. - PubMed
-
- Lei H, Hu J, Sun K, Xu D. The role and molecular mechanism of epigenetics in cardiac hypertrophy. Heart Fail Rev 2021;26:1505-14. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

