Lymphatics act as a signaling hub to regulate intestinal stem cell activity
- PMID: 35728595
- PMCID: PMC9271639
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2022.05.007
Lymphatics act as a signaling hub to regulate intestinal stem cell activity
Abstract
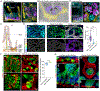
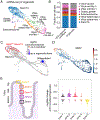
Barrier epithelia depend upon resident stem cells for homeostasis, defense, and repair. Epithelial stem cells of small and large intestines (ISCs) respond to their local microenvironments (niches) to fulfill a continuous demand for tissue turnover. The complexity of these niches and underlying communication pathways are not fully known. Here, we report a lymphatic network at the intestinal crypt base that intimately associates with ISCs. Employing in vivo loss of function and lymphatic:organoid cocultures, we show that crypt lymphatics maintain ISCs and inhibit their precocious differentiation. Pairing single-cell and spatial transcriptomics, we apply BayesPrism to deconvolve expression within spatial features and develop SpaceFold to robustly map the niche at high resolution, exposing lymphatics as a central signaling hub for the crypt in general and ISCs in particular. We identify WNT-signaling factors (WNT2, R-SPONDIN-3) and a hitherto unappreciated extracellular matrix protein, REELIN, as crypt lymphatic signals that directly govern the regenerative potential of ISCs.
Keywords: REELIN; RSPO3; WNTs; intestinal stem cells; lymphatic:stem cell interactome; lymphatics; organoids; spatial deconvolution; spatial transcriptomics of murine large and small intestine; stem cell niches.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests D.P. is on the scientific advisory board of Insitro. B.J.M. is an advisor to and recipient of an investigator-initiated research award from PureTech Corp. and recipient of an investigator-initiated research award from Regeneron. E.F. served on the scientific advisory boards of Arsenal Biosciences and L’Oreal.
Figures




Comment in
-
Lymphatic endothelia stakeout cryptic stem cells.Cell Stem Cell. 2022 Sep 1;29(9):1292-1293. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2022.08.006. Cell Stem Cell. 2022. PMID: 36055189
References
-
- Alexander JS, Chaitanya GV, Grisham MB, and Boktor M (2010). Emerging roles of lymphatics in inflammatory bowel disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci 1207, E75–E85. - PubMed
-
- Baccin C, Al-Sabah J, Velten L, Helbling PM, Grünschläger F, Hernández-Malmierca P, Nombela-Arrieta C, Steinmetz LM, Trumpp A, and Haas S (2019). Combined single-cell and spatial transcriptomics reveal the molecular, cellular and spatial bone marrow niche organization. Nat. Cell Biol 2019 221 22, 38–48. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baghdadi MB, Ayyaz A, Coquenlorge S, Chu B, Kumar S, Streutker C, Wrana JL, and Kim T-H (2021). Enteric glial cell heterogeneity regulates intestinal stem cell niches. Cell Stem Cell 29, 1–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

