Magnetoencephalography biomarkers of suicide attempt history and antidepressant response to ketamine in treatment-resistant major depression
- PMID: 35728680
- PMCID: PMC9262873
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.06.025
Magnetoencephalography biomarkers of suicide attempt history and antidepressant response to ketamine in treatment-resistant major depression
Abstract
Background: This study examined magnetoencephalographic (MEG) correlates of suicidal ideation (SI) and suicide attempt history in patients with treatment-resistant major depression (TRD) at baseline and following subanesthetic-dose ketamine infusion.
Methods: Twenty-nine drug-free TRD patients (12 suicide attempters/17 non-attempters) participated in a crossover randomized trial of ketamine. MEG data were collected during an attentional dot probe task with emotional face stimuli at baseline and several hours post-ketamine infusion. Synthetic aperture magnetometry was used to project source power in the theta, alpha, beta, and gamma frequencies for angry-neutral, happy-neutral, and neutral-neutral face pairings during a one-second peristimulus period. Mixed models were used to test for clinical, behavioral, and electrophysiological effects of group, emotion, session, and SI score.
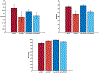
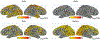
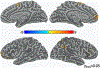
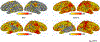
Results: Ketamine significantly reduced SI and depression across the sample. Post-ketamine, attempters had improved accuracy and non-attempters had reduced accuracy on the task. SI was positively associated with gamma power in regions of the frontal and parietal cortices across groups. In an extended amygdala-hippocampal region, attempters differed significantly in their emotional reactivity to angry versus happy faces as indexed by theta power differences, irrespective of drug. Ketamine significantly reduced the association between alpha power and SI for angry compared with happy faces in a fronto-insular/anterior cingulate region important for regulating sensory attentiveness.
Limitations: Limitations include a small sample size of attempters.
Conclusions: The findings highlight key differences in band-limited power between attempters and non-attempters and reinforce previous findings that ketamine has distinct response properties in patients with a suicide history.
Keywords: Ketamine; Magnetoencephalography; Suicidal ideation; Suicide attempt; Treatment-resistant depression.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interest
Dr. Zarate is listed as a co-inventor on a patent for the use of ketamine in major depression and suicidal ideation; as a co-inventor on a patent for the use of (2
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

