Identification of structurally re-engineered rocaglates as inhibitors against hepatitis E virus replication
- PMID: 35728703
- PMCID: PMC9731315
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105359
Identification of structurally re-engineered rocaglates as inhibitors against hepatitis E virus replication
Abstract
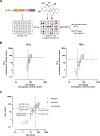
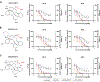
Hepatitis E virus (HEV) infections are a leading cause of acute viral hepatitis in humans and pose a considerable threat to public health. Current standard of care treatment is limited to the off-label use of nucleoside-analog ribavirin (RBV) and PEGylated interferon-α, both of which are associated with significant side effects and provide limited efficacy. In the past few years, a promising natural product compound class of eukaryotic initiation factor 4A (eIF4A) inhibitors (translation initiation inhibitors), called rocaglates, were identified as antiviral agents against RNA virus infections. In the present study, we evaluated a total of 205 synthetic rocaglate derivatives from the BU-CMD compound library for their antiviral properties against HEV. At least eleven compounds showed inhibitory activities against the HEV genotype 3 (HEV-3) subgenomic replicon below 30 nM (EC50 value) as determined by Gaussia luciferase assay. Three amidino-rocaglates (ADRs) (CMLD012073, CMLD012118, and CMLD012612) possessed antiviral activity against HEV with EC50 values between 1 and 9 nM. In addition, these three selected compounds inhibited subgenomic replicons of different genotypes (HEV-1 [Sar55], wild boar HEV-3 [83-2] and human HEV-3 [p6]) in a dose-dependent manner and at low nanomolar concentrations. Furthermore, tested ADRs tend to be better tolerated in primary hepatocytes than hepatoma cancer cell lines and combination treatment of CMLD012118 with RBV and interferon-α (IFN-α) showed that CMLD012118 acts additive to RBV and IFN-α treatment. In conclusion, our results indicate that ADRs, especially CMLD012073, CMLD012118, and CMLD012612 may prove to be potential therapeutic candidates for the treatment of HEV infections and may contribute to the discovery of pan-genotypic inhibitors in the future.
Keywords: Amidino-rocaglates; Antiviral treatment; Antivirals; Hepatitis E virus; elF4A inhibitors.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
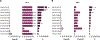
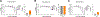
Similar articles
-
The natural compound silvestrol inhibits hepatitis E virus (HEV) replication in vitro and in vivo.Antiviral Res. 2018 Sep;157:151-158. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.07.010. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Antiviral Res. 2018. PMID: 30036559 Free PMC article.
-
Ribavirin Treatment Failure-Associated Mutation, Y1320H, in the RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase of Genotype 3 Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) Enhances Virus Replication in a Rabbit HEV Infection Model.mBio. 2023 Apr 25;14(2):e0337222. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03372-22. Epub 2023 Feb 21. mBio. 2023. PMID: 36809085 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral Activities of Different Interferon Types and Subtypes against Hepatitis E Virus Replication.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Mar 25;60(4):2132-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02427-15. Print 2016 Apr. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 26787701 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis E virus treatment and ribavirin therapy: viral mechanisms of nonresponse.Curr Opin Virol. 2018 Oct;32:80-87. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2018.10.001. Epub 2018 Oct 29. Curr Opin Virol. 2018. PMID: 30384328 Review.
-
Mutagenic Effects of Ribavirin on Hepatitis E Virus-Viral Extinction versus Selection of Fitness-Enhancing Mutations.Viruses. 2016 Oct 13;8(10):283. doi: 10.3390/v8100283. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27754363 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of RNA-Protein Molecular Clamps Using Proteome-Wide Stability Assays.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 21:2024.04.19.590252. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.19.590252. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Proteome Res. 2025 Apr 04;24(4):2026-2039. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.4c01129. PMID: 38659867 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Amidino-rocaglates (ADRs), a class of synthetic rocaglates, are potent inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 replication through inhibition of viral protein synthesis.Antiviral Res. 2024 Oct;230:105976. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2024.105976. Epub 2024 Aug 6. Antiviral Res. 2024. PMID: 39117283
-
PDCD4 restricts PRRSV replication in an eIF4A-dependent manner and is antagonized by the viral nonstructural protein 9.J Virol. 2024 May 14;98(5):e0006024. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00060-24. Epub 2024 Apr 1. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38557170 Free PMC article.
-
A parasitic fungus employs mutated eIF4A to survive on rocaglate-synthesizing Aglaia plants.Elife. 2023 Feb 28;12:e81302. doi: 10.7554/eLife.81302. Elife. 2023. PMID: 36852480 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Basis for the Improved RNA Clamping of Amidino-Rocaglates to eIF4A1.ACS Omega. 2025 Feb 10;10(6):5795-5808. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c09421. eCollection 2025 Feb 18. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 39989799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chan K, Robert F, Oertlin C, Kapeller-Libermann D, Avizonis D, Gutierrez J, Handly-Santana A, Doubrovin M, Park J, Schoepfer C, Da Silva B, Yao M, Gorton F, Shi J, Thomas CJ, Brown LE, Porco JA, Pollak M, Larsson O, Pelletier J, Chio IIC, 2019. eIF4A supports an oncogenic translation program in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Nat Commun 10, 5151. 10.1038/s41467-019-13086-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

