Investigation of the use of a sensor bracelet for the presymptomatic detection of changes in physiological parameters related to COVID-19: an interim analysis of a prospective cohort study (COVI-GAPP)
- PMID: 35728900
- PMCID: PMC9240454
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-058274
Investigation of the use of a sensor bracelet for the presymptomatic detection of changes in physiological parameters related to COVID-19: an interim analysis of a prospective cohort study (COVI-GAPP)
Abstract
Objectives: We investigated machinelearningbased identification of presymptomatic COVID-19 and detection of infection-related changes in physiology using a wearable device.
Design: Interim analysis of a prospective cohort study.
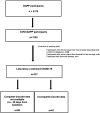
Setting, participants and interventions: Participants from a national cohort study in Liechtenstein were included. Nightly they wore the Ava-bracelet that measured respiratory rate (RR), heart rate (HR), HR variability (HRV), wrist-skin temperature (WST) and skin perfusion. SARS-CoV-2 infection was diagnosed by molecular and/or serological assays.
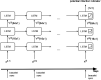
Results: A total of 1.5 million hours of physiological data were recorded from 1163 participants (mean age 44±5.5 years). COVID-19 was confirmed in 127 participants of which, 66 (52%) had worn their device from baseline to symptom onset (SO) and were included in this analysis. Multi-level modelling revealed significant changes in five (RR, HR, HRV, HRV ratio and WST) device-measured physiological parameters during the incubation, presymptomatic, symptomatic and recovery periods of COVID-19 compared with baseline. The training set represented an 8-day long instance extracted from day 10 to day 2 before SO. The training set consisted of 40 days measurements from 66 participants. Based on a random split, the test set included 30% of participants and 70% were selected for the training set. The developed long short-term memory (LSTM) based recurrent neural network (RNN) algorithm had a recall (sensitivity) of 0.73 in the training set and 0.68 in the testing set when detecting COVID-19 up to 2 days prior to SO.
Conclusion: Wearable sensor technology can enable COVID-19 detection during the presymptomatic period. Our proposed RNN algorithm identified 68% of COVID-19 positive participants 2 days prior to SO and will be further trained and validated in a randomised, single-blinded, two-period, two-sequence crossover trial. Trial registration number ISRCTN51255782; Pre-results.
Keywords: COVID-19; Health & safety; Health informatics; Infection control; Public health; VIROLOGY.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: LR, and MR are key shareholders of the Dr Risch Medical Laboratory. DC has received consulting fees from Roche Diagnostics, outside of the current work. MR, DL, VK, AM, MC, and BMG are employed by Ava AG. The other authors have no financial or personal conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
-
- WHO . WHO_weekly-operational-update-on-covid-19-29-march-2021, 2021. Available: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-operational-update-on-cov... [Accessed March 30, 2021].
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Similarities and difference between flu and COVID-19 [Accessed March 2021].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
