Caveolar and non-Caveolar Caveolin-1 in ocular homeostasis and disease
- PMID: 35729002
- PMCID: PMC9669151
- DOI: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2022.101094
Caveolar and non-Caveolar Caveolin-1 in ocular homeostasis and disease
Abstract
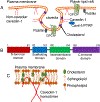
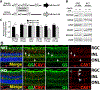
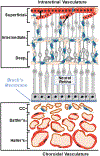
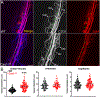
Caveolae, specialized plasma membrane invaginations present in most cell types, play important roles in multiple cellular processes including cell signaling, lipid uptake and metabolism, endocytosis and mechanotransduction. They are found in almost all cell types but most abundant in endothelial cells, adipocytes and fibroblasts. Caveolin-1 (Cav1), the signature structural protein of caveolae was the first protein associated with caveolae, and in association with Cavin1/PTRF is required for caveolae formation. Genetic ablation of either Cav1 or Cavin1/PTRF downregulates expression of the other resulting in loss of caveolae. Studies using Cav1-deficient mouse models have implicated caveolae with human diseases such as cardiomyopathies, lipodystrophies, diabetes and muscular dystrophies. While caveolins and caveolae are extensively studied in extra-ocular settings, their contributions to ocular function and disease pathogenesis are just beginning to be appreciated. Several putative caveolin/caveolae functions are relevant to the eye and Cav1 is highly expressed in retinal vascular and choroidal endothelium, Müller glia, the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), and the Schlemm's canal endothelium and trabecular meshwork cells. Variants at the CAV1/2 gene locus are associated with risk of primary open angle glaucoma and the high risk HTRA1 variant for age-related macular degeneration is thought to exert its effect through regulation of Cav1 expression. Caveolins also play important roles in modulating retinal neuroinflammation and blood retinal barrier permeability. In this article, we describe the current state of caveolin/caveolae research in the context of ocular function and pathophysiology. Finally, we discuss new evidence showing that retinal Cav1 exists and functions outside caveolae.
Keywords: Caveolae; Caveolin; Cavin1/PTRF; Glaucoma; Inflammation; Müller glia; Non-caveolar Cav1; Retina; Retinal vasculature.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
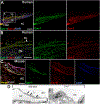
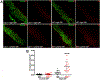
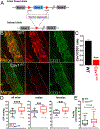
Figures
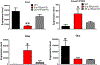

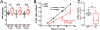
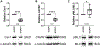
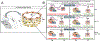

References
-
- Abbasi M, Gupta VK, Chitranshi N, Gupta V, Ranjbaran R, Rajput R, Pushpitha K, Kb D, You Y, Salekdeh GH, Parton RG, Mirzaei M, Graham SL, 2021. Inner retinal injury in experimental glaucoma is prevented upon AAV mediated Shp2 silencing in a caveolin dependent manner. Theranostics 11, 6154–6172. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abbasi M, Gupta VK, Chitranshi N, Gupta VB, Mirzaei M, Dheer Y, Garthwaite L, Zaw T, Parton RG, You Y, Graham SL, 2020. Caveolin-1 ablation imparts partial protection against inner retinal injury in experimental glaucoma and reduces apoptotic activation. Mol. Neurobiol 57, 3759–3784. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

