First-line single-agent pembrolizumab for PD-L1-positive (tumor proportion score ≥ 50%) advanced non-small cell lung cancer in the real world: impact in brain metastasis: a national French multicentric cohort (ESCKEYP GFPC study)
- PMID: 35729418
- PMCID: PMC10992810
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-022-03232-2
First-line single-agent pembrolizumab for PD-L1-positive (tumor proportion score ≥ 50%) advanced non-small cell lung cancer in the real world: impact in brain metastasis: a national French multicentric cohort (ESCKEYP GFPC study)
Abstract
Background: Few real-world data are available in patients with advanced metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with first-line immunotherapy, particularly in those with brain metastases at treatment initiation.
Methods: This was a national, retrospective, multicenter study that consecutively included all patients with PD-L1-positive (tumor proportion score ≥ 50%) advanced NSCLC who initiated first-line treatment with pembrolizumab as a single agent between May 2017 (date of availability of pembrolizumab in this indication in France) to November 22, 2019 (approval of the pembrolizumab-chemotherapy combination). Data were collected from medical records with local response assessment.
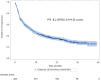
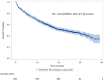
Results: The cohort included 845 patients and 176 (20.8%) had brain metastases at diagnosis. There were no significant differences in outcomes for patients with and without brain metastases: 9.2 (95% CI 5.6-15) and 8 (95% CI 6.7-9.2, p = 0.3) months for median progression-free survival (PFS) and, 29.5 (95% CI 17.2-NA) and 22 (95% CI 17.8-27.1, p = 0.3) months for median overall survival (OS), respectively. Overall response rates were 47% and 45% in patients with and without cerebral metastases. In multivariate analysis, performance status 2-4 vs. 0-1 and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio ≥ 4 vs. < 4 were the main independent negative factors for OS; brain metastasis was not an independent factor for OS.
Conclusion: In this large multicenter cohort, nearly 20% of patients initiating pembrolizumab therapy for advanced NSCLC had cerebral metastases. There was no significant difference in response rates, PFS and OS between patients with and without brain metastases.
Keywords: Advanced stage; Brain metastases; Non-small cell lung cancer; Pembrolizumab; Real-world study.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
L. Greillier reports grants, personal fees and non-financial support from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Roche, Sanofi Aventis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Takeda, Bayer and Amgen, outside the submitted work. C. Chouaid reports grants, personal fees and non-financial support from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, GSK, Roche, Sanofi Aventis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Takeda, Bayer and Amgen, outside the submitted work. C. Decroisette reports personal fees and non-financial support from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Roche, Sanofi Aventis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Takeda, and Amgen, outside the submitted work. M. Pérol reports personal fees and non-financial support from Roche, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, AstraZeneca, Takeda, Gritstone, Sanofi, GlaxoSmithKline, Amgen, Chugai, Illumina, Daïchi-Sankyo and Abbvie outside the submitted work. R. Descourt reports personal fees and non-financial support from AstraZeneca, Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pfizer, Takeda, and Chugai, outside the submitted work. C. Ricordel, J.B. Auliac, L. Falchero, R. Gervais, R. Veillon, S. Vieillot, F. Guisier, M. Marcq, G. Justeau, L. Bigay-Game, M. Bernardi, P. Fournel, H. Doubre, J. Pinsolle and K. Amrane report no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Institut National du Cancer (2016) Accès aux tests moléculaires EGFR, RAS et BRAF. Résultats d’une enquête dans 5 régions françaises
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials