The clinicopathological and prognostic value of CXCR4 expression in patients with lung cancer: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 35729596
- PMCID: PMC9210617
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-022-09756-1
The clinicopathological and prognostic value of CXCR4 expression in patients with lung cancer: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The C-X-C chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) has been suggested to play an important role in several types of cancers and is related to biological behaviors connected with tumor progression. However, the clinical significance and application of CXCR4 in lung cancer remain disputable. Thus, we conducted a meta-analysis to investigate the impact of CXCR4 expression on survival and clinicopathological features in lung cancer.
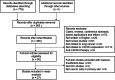
Methods: Comprehensive literature searches were conducted in PubMed, Embase and Web of Science for relevant studies. We pooled hazard ratios (HRs)/odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) by STATA 12.0 to evaluate the potential value of CXCR4 expression.
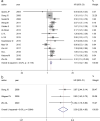
Results: Twenty-seven relevant articles involving 2932 patients with lung cancer were included in our meta-analysis. The results revealed that CXCR4 expression was apparently associated with poor overall survival (OS) (HR 1.61, 95% CI 1.42-1.82) and disease-free survival (HR 3.39, 95% CI 2.38-4.83). Furthermore, a significant correlation with poor OS was obvious in non-small cell lung cancer patients (HR 1.59, 95% CI 1.40-1.81) and in patients showing CXCR4 expression in the cytoplasm (HR 2.10, 95% CI 1.55-2.84) and the membrane (HR 1.74, 95% CI 1.24-2.45). CXCR4 expression was significantly associated with men (OR 1.32, 95% CI 1.08-1.61), advanced tumor stages (T3-T4) (OR 2.34, 95% CI 1.28-4.28), advanced nodal stages (N > 0) (OR 2.34, 95% CI 1.90-2.90), distant metastasis (OR 3.65, 95% CI 1.53-8.69), advanced TNM stages (TNM stages III, IV) (OR 3.10, 95% CI 1.95-4.93) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression (OR 2.44, 95% CI 1.44-4.12) but was not associated with age, smoking history, histopathology, differentiation, lymphatic vessel invasion or local recurrence.
Conclusion: High expression of CXCR4 is related to tumor progression and might be an adverse prognostic factor for lung cancer.
Keywords: CXCR4; Clinicopathological features; Lung cancer; Meta-analysis; Prognosis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2017, National Cancer Institute, National Cancer Institute. 2019. https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2017/ . Accessed 30 April 2020.
-
- Saintigny P, Burger JA. Recent advances in non-small cell lung cancer biology and clinical management. Discov Med. 2012;13(71):287–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

