MiR-106a facilitates the sensorineural hearing loss induced by oxidative stress by targeting connexin-43
- PMID: 35730503
- PMCID: PMC9342191
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2071021
MiR-106a facilitates the sensorineural hearing loss induced by oxidative stress by targeting connexin-43
Abstract
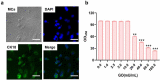
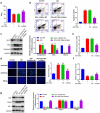
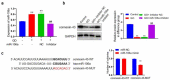
Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is a common clinical side effect resulted from the overusing of aminoglycoside antibacterial drugs, such as gentamicin. Oxidative stress is recently evidenced to be an important inducer for SNHL, which is reported to be associated with the knockdown of connexin-43. MiR-106a is recently found as a regulator of connexin-43. The present study aims to investigate whether miR-106a is a vital mediator in the development of SNHL. Firstly, upregulated miR-106a was observed in the peripheral blood sample of SNHL patients. Glucose oxidase (GO) was utilized to induce oxidative injury in isolated rat cochlear marginal cells (MCs), followed by introducing the miR-106a inhibitor. We found that the declined proliferation ability, increased apoptosis, and activated oxidative stress in GO-stimulated MCs were dramatically abolished by the miR-106a inhibitor, accompanied by the upregulation of connexin-43. The targeting correlation between miR-106a and connexin-43 was predicted and confirmed by the dual luciferase gene reporter assay. Furthermore, the regulatory effect of miR-106a inhibitor against the proliferation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress in GO-treated MCs were dramatically abolished by the knockdown of connexin-43. Gentamicin was utilized to establish the SNHL model in rats, followed by the treatments of antagomir-106a and antagomir-106a combined with carbenoxolone, an inhibitor of connexin-43. The alleviated pathological state, reduced apoptosis, and ameliorated oxidative stress in cochlea tissues were observed in antagomir-106a treated SNHL rats, which were dramatically reversed by the co-administration of carbenoxolone. Collectively, miR-106a facilitated the SNHL induced by oxidative stress via targeting connexin-43.
Keywords: MiR-106a; connexin-43; oxidative stress; sensorineural hearing loss.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-106a functions as an oncogene in human gastric cancer and contributes to proliferation and metastasis in vitro and in vivo.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2016 Jun;33(5):509-19. doi: 10.1007/s10585-016-9795-9. Epub 2016 May 3. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2016. PMID: 27142596
-
MicroRNA-106a regulates the apoptosis and oxidative stress of porcine trabecular meshwork cells by targeting FAS.Exp Eye Res. 2025 May;254:110313. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2025.110313. Epub 2025 Mar 1. Exp Eye Res. 2025. PMID: 40032150
-
miR-106a promotes cardiac hypertrophy by targeting mitofusin 2.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016 Oct;99:207-217. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.08.016. Epub 2016 Aug 23. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27565029
-
The role of hypoxia-associated miRNAs in acquired sensorineural hearing loss.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Aug 5;16:916696. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.916696. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35990888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs in Noise-Induced Hearing Loss and their Regulation by Oxidative Stress and Inflammation.Curr Drug Targets. 2020;21(12):1216-1224. doi: 10.2174/1389450121666200615145552. Curr Drug Targets. 2020. PMID: 32538724 Review.
Cited by
-
miR-145b/AP2B1 Axis Contributes to Noise-induced Sensorineural Hearing Loss In a Male Mouse Model.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Jun;83(2):2567-2575. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01665-3. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 39813009
-
Acquired sensorineural hearing loss, oxidative stress, and microRNAs.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Sep 1;20(9):2513-2519. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00579. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 39314173 Free PMC article.
-
ANXA1sp attenuates sepsis-induced myocardial injury by promoting mitochondrial biosynthesis and inhibiting oxidative stress and autophagy via SIRT3 upregulation.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2024 Jan;40(1):35-45. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12767. Epub 2023 Oct 25. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 37877496 Free PMC article.
-
NcRNA: key and potential in hearing loss.Front Neurosci. 2024 Jan 17;17:1333131. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1333131. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38298898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential Role of Connexins in the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 30;24(3):2600. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032600. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768920 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang DT, Ramakrishnaiah R, Kanfi A.. Sensorineural hearing loss through the ages. Semin Roentgenol. 2019;54(3):207–214. - PubMed
-
- Liu H, Zhou K, Zhang X, et al. Fluctuating sensorineural hearing loss. Audiol Neurootol. 2019;24(3):109–116. - PubMed
-
- Celik M, Koyuncu İ. Oxidative stress in prelingual sensorineural hearing loss and the effects of cochlear implant application on serum oxidative stress levels. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2019;119:177–182. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
