Presentation and outcomes of patients with clinically T1-2, N0 parotid mucoepidermoid carcinoma: The roles of elective neck dissection and adjuvant radiotherapy
- PMID: 35731030
- PMCID: PMC9544346
- DOI: 10.1002/hed.27128
Presentation and outcomes of patients with clinically T1-2, N0 parotid mucoepidermoid carcinoma: The roles of elective neck dissection and adjuvant radiotherapy
Abstract
Objectives: Examine the role of elective neck dissection (END) and adjuvant radiotherapy (RT) in early-stage clinically N0 parotid mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC).
Methods: The study is a retrospective analysis of the National Cancer Database, 2004-2016. The study population included adult patients with MEC who underwent parotidectomy.
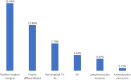
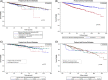
Results: A total of 1233 patients were included. Histopathology demonstrated well, moderately, and poorly differentiated MEC 47.12%, 39.98%, and 12.90% of the time, respectively. END was performed in 78.67% of patients, resulting in nodal upstaging in 4.43% and identification of extracapsular extension (ECE) in 0.72%. RT was utilized in 67.33% of patients with advanced pathological features. Neither END nor RT improved overall survival separately (p < 0.05) or combined (adjusted HR: 1.19, 95%CI: 0.52, 2.70, p = 0.68).
Conclusion: This study provides an epidemiological perspective regarding patients with clinically T1-2, N0 MEC. There was no observed survival advantage with END and RT.
Keywords: epidemiology; facial nerve; mucoepidermoid carcinoma; neck dissection; parotidectomy; radiotherapy; survival.
© 2022 The Authors. Head & Neck published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Survival Impact of Elective Neck Dissection and Adjuvant Radiation in N0 High-Grade Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024 Jul;171(1):138-145. doi: 10.1002/ohn.695. Epub 2024 Mar 1. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024. PMID: 38426623
-
Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma of the Parotid: Very Close Margins and Adjuvant Radiotherapy.ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2019;81(1):55-62. doi: 10.1159/000497438. Epub 2019 Apr 2. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2019. PMID: 30939481
-
Elective nodal dissection for cN0 intermediate-grade parotid mucoepidermoid carcinoma: A NCDB study.Am J Otolaryngol. 2024 May-Jun;45(3):104214. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2023.104214. Epub 2024 Jan 6. Am J Otolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 38218029
-
What is the role of elective neck dissection in low-, intermediate-, and high-grade mucoepidermoid carcinoma?Laryngoscope. 2016 Jan;126(1):11-3. doi: 10.1002/lary.25588. Epub 2015 Sep 7. Laryngoscope. 2016. PMID: 26344690 Review. No abstract available.
-
Elective neck dissection in T1/T2 oral squamous cell carcinoma with N0 neck: essential or not? A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020 Jun;277(6):1741-1752. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-05866-3. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020. PMID: 32100133
Cited by
-
Neck Dissection in cT3/T4 Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma of the Oral Cavity and Oropharynx.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024 Oct;76(5):4163-4170. doi: 10.1007/s12070-024-04808-3. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024. PMID: 39376357 Free PMC article.
-
Elective Neck Dissection in cT1-4 N0M0 Head and Neck Spindle Cell Carcinoma.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2025 Aug;173(2):433-446. doi: 10.1002/ohn.1265. Epub 2025 Apr 21. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2025. PMID: 40257327 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical Treatment of Carcinomas of the Oral Minor Salivary Glands-Oncological Outcome in Dependence of Tumor Entity and Therapeutic Strategies.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jul 31;15(15):3895. doi: 10.3390/cancers15153895. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37568711 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

