Optimal target saturation of ligand-blocking anti-GITR antibody IBI37G5 dictates FcγR-independent GITR agonism and antitumor activity
- PMID: 35732156
- PMCID: PMC9245059
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100660
Optimal target saturation of ligand-blocking anti-GITR antibody IBI37G5 dictates FcγR-independent GITR agonism and antitumor activity
Abstract
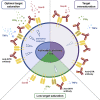
Glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor (GITR) is a co-stimulatory receptor and an important target for cancer immunotherapy. We herein present a potent FcγR-independent GITR agonist IBI37G5 that can effectively activate effector T cells and synergize with anti-programmed death 1 (PD1) antibody to eradicate established tumors. IBI37G5 depends on both antibody bivalency and GITR homo-dimerization for efficient receptor cross-linking. Functional analyses reveal bell-shaped dose responses due to the unique 2:2 antibody-receptor stoichiometry required for GITR activation. Antibody self-competition is observed after concentration exceeded that of 100% receptor occupancy (RO), which leads to antibody monovalent binding and loss of activity. Retrospective pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics analysis demonstrates that the maximal efficacy is achieved at medium doses with drug exposure near saturating GITR occupancy during the dosing cycle. Finally, we propose an alternative dose-finding strategy that does not rely on the traditional maximal tolerated dose (MTD)-based paradigm but instead on utilizing the RO-function relations as biomarker to guide the clinical translation of GITR and similar co-stimulatory agonists.
Keywords: GITR; agonist antibody; cancer immunotherapy; costimulatory receptor; receptor occupancy.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests H.L., W.W., T.C., L.C., X.L., J.G., F.F., Y.Y., Z. Wu, S.Z., J.W., J.L., Z.K., M.W., Z.S., L.H., D.W., B.C., and K.H. are current employees and own stocks of Innovent Biologics (Suzhou) Co., Ltd. F.F. is co-inventor of GITR antibodies used in this study (patent no. WO2019201301A1).
Figures




References
-
- van Beek A.A., Zhou G., Doukas M., Boor P.P.C., Noordam L., Mancham S., Campos Carrascosa L., van der Heide-Mulder M., Polak W.G., Ijzermans J.N.M., et al. GITR ligation enhances functionality of tumor-infiltrating T cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer. 2019;145:1111–1124. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32181. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

