Women are credited less in science than men
- PMID: 35732238
- PMCID: PMC9352587
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04966-w
Women are credited less in science than men
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Women are credited less in science than men.Nature. 2023 Sep;621(7979):E41. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06571-x. Nature. 2023. PMID: 37658202 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
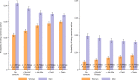
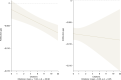
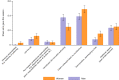
There is a well-documented gap between the observed number of works produced by women and by men in science, with clear consequences for the retention and promotion of women1. The gap might be a result of productivity differences2-5, or it might be owing to women's contributions not being acknowledged6,7. Here we find that at least part of this gap is the result of unacknowledged contributions: women in research teams are significantly less likely than men to be credited with authorship. The findings are consistent across three very different sources of data. Analysis of the first source-large-scale administrative data on research teams, team scientific output and attribution of credit-show that women are significantly less likely to be named on a given article or patent produced by their team relative to their male peers. The gender gap in attribution is present across most scientific fields and almost all career stages. The second source-an extensive survey of authors-similarly shows that women's scientific contributions are systematically less likely to be recognized. The third source-qualitative responses-suggests that the reason that women are less likely to be credited is because their work is often not known, is not appreciated or is ignored. At least some of the observed gender gap in scientific output may be owing not to differences in scientific contribution, but rather to differences in attribution.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Probe how race and gender intersect in author attribution.Nature. 2022 Nov;611(7934):33. doi: 10.1038/d41586-022-03516-8. Nature. 2022. PMID: 36319760 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Tomaskovic-Devey D. Women’s work: gender equality vs. hierarchy in the life sciences. Adm. Sci. Q. 2005;50:661–662. doi: 10.2189/asqu.50.4.661. - DOI
-
- Whittington KB, Smith-Doerr L. Gender and commercial science: women’s patenting in the life sciences. J. Technol. Transf. 2005;30:355–370. doi: 10.1007/s10961-005-2581-5. - DOI
-
- Mairesse J, Pezzoni M. Does gender affect scientific productivity? Rev. Écon. 2015;66:65–113. doi: 10.3917/reco.661.0065. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

