PIEZO1 transduces mechanical itch in mice
- PMID: 35732741
- PMCID: PMC9259491
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04860-5
PIEZO1 transduces mechanical itch in mice
Abstract
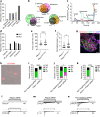
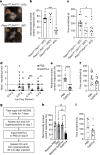
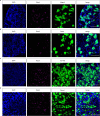
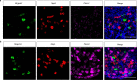
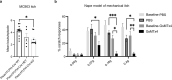
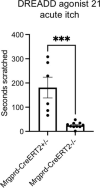
Itch triggers scratching, a behavioural defence mechanism that aids in the removal of harmful irritants and parasites1. Chemical itch is triggered by many endogenous and exogenous cues, such as pro-inflammatory histamine, which is released during an allergic reaction1. Mechanical itch can be triggered by light sensations such as wool fibres or a crawling insect2. In contrast to chemical itch pathways, which have been extensively studied, the mechanisms that underlie the transduction of mechanical itch are largely unknown. Here we show that the mechanically activated ion channel PIEZO1 (ref. 3) is selectively expressed by itch-specific sensory neurons and is required for their mechanically activated currents. Loss of PIEZO1 function in peripheral neurons greatly reduces mechanically evoked scratching behaviours and both acute and chronic itch-evoked sensitization. Finally, mice expressing a gain-of-function Piezo1 allele4 exhibit enhanced mechanical itch behaviours. Our studies reveal the polymodal nature of itch sensory neurons and identify a role for PIEZO1 in the sensation of itch.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Comment in
-
Touch-evoked itch pinned on Piezo1 ion-channel protein.Nature. 2022 Jul;607(7917):36-37. doi: 10.1038/d41586-022-01571-9. Nature. 2022. PMID: 35732710 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lay M, Dong X. Neural mechanisms of itch. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2020;43:187–205. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

