Antennal transcriptome analysis of olfactory genes and tissue expression profiling of odorant binding proteins in Semanotus bifasciatus (cerambycidae: coleoptera)
- PMID: 35733103
- PMCID: PMC9219211
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-022-08655-w
Antennal transcriptome analysis of olfactory genes and tissue expression profiling of odorant binding proteins in Semanotus bifasciatus (cerambycidae: coleoptera)
Abstract
Background: Insect olfactory proteins can transmit chemical signals in the environment that serve as the basis for foraging, mate searching, predator avoidance and oviposition selection. Semanotus bifasciatus is an important destructive borer pest, but its olfactory mechanism is not clear. We identified the chemosensory genes of S. bifasciatus in China, then we conducted a phylogenetic analysis of the olfactory genes of S. bifasciatus and other species. And the expression profiles of odorant binding proteins (OBPs) genes in different tissues and different genders of S. bifasciatus were determined by quantitative real-time PCR for the first time.
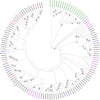
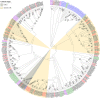
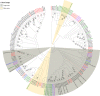
Results: A total of 32 OBPs, 8 chemosensory proteins (CSPs), 71 odorant receptors (ORs), 34 gustatory receptors (GRs), 18 ionotropic receptors (IRs), and 3 sensory neuron membrane proteins (SNMPs) were identified. In the tissue expression analysis of OBP genes, 7 OBPs were higher expressed in antennae, among them, SbifOBP2, SbifOBP3, SbifOBP6, SbifOBP7 and SbifOBP20 were female-biased expression, while SbifOBP1 was male-biased expression and SbifOBP22 was no-biased expression in antennae. In addition, the expressed levels of SbifOBP4, SbifOBP12, SbifOBP15, SbifOBP27 and SbifOBP29 were very poor in the antennae, and SbifOBP4 and SbifOBP29 was abundant in the head or legs, and both of them were male-biased expression. While SbifOBP15 was highly expressed only at the end of the abdomen with its expression level in females three times than males. Other OBPs were expressed not only in antennae but also in various tissues.
Conclusion: We identified 166 olfactory genes from S. bifasciatus, and classified these genes into groups and predicted their functions by phylogenetic analysis. The majority of OBPs were antenna-biased expressed, which are involved in odor recognition, sex pheromone detection, and/or host plant volatile detection. However, also some OBPs were detected biased expression in the head, legs or end of the abdomen, indicating that they may function in the different physiological processes in S. bifasciatus.
Keywords: Antennal transcriptome; Odorant binding protein; Semanotus bifasciatus; Tissue expression profiles.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Antennal transcriptome analysis of olfactory genes and characterizations of odorant binding proteins in two woodwasps, Sirex noctilio and Sirex nitobei (Hymenoptera: Siricidae).BMC Genomics. 2021 Mar 10;22(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07452-1. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33691636 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of chemosensory genes in the antennal transcriptome of Spodoptera exigua.Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics. 2018 Sep;27:54-65. doi: 10.1016/j.cbd.2018.05.001. Epub 2018 May 7. Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics. 2018. PMID: 29787920
-
Antennal transcriptome analysis and expression profiles of odorant binding proteins in Eogystia hippophaecolus (Lepidoptera: Cossidae).BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 18;17:651. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3008-4. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27538507 Free PMC article.
-
The role of SNMPs in insect olfaction.Cell Tissue Res. 2021 Jan;383(1):21-33. doi: 10.1007/s00441-020-03336-0. Epub 2020 Nov 27. Cell Tissue Res. 2021. PMID: 33245414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Odorant-binding proteins of mammals.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2022 Feb;97(1):20-44. doi: 10.1111/brv.12787. Epub 2021 Sep 3. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2022. PMID: 34480392 Review.
Cited by
-
A Review of the Host Plant Location and Recognition Mechanisms of Asian Longhorn Beetle.Insects. 2023 Mar 17;14(3):292. doi: 10.3390/insects14030292. Insects. 2023. PMID: 36975977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering the Olfactory Mechanisms of Sitotroga cerealella Olivier (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae): Insights from Transcriptome Analysis and Molecular Docking.Insects. 2025 Apr 27;16(5):461. doi: 10.3390/insects16050461. Insects. 2025. PMID: 40429174 Free PMC article.
-
A Highly Expressed Antennae Odorant-Binding Protein Involved in Recognition of Herbivore-Induced Plant Volatiles in Dastarcus helophoroides.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 9;24(4):3464. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043464. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834874 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Expression Profiles of Chemosensory Genes in the Antennal Transcriptome of Protaetia brevitarsis (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae).Insects. 2025 Jun 9;16(6):607. doi: 10.3390/insects16060607. Insects. 2025. PMID: 40559037 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angeli S, Ceron F, Scaloni A, Monti M, Monteforti G, Minnocci A, et al. Purification, structural characterization, cloning and immunocytochemical localization of chemoreception proteins from Schistocerca gregaria. Eur J Biochem. 1999;262(3):745–754. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00438.x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

