Bartha-K61 vaccine protects nursery pigs against challenge with novel european and asian strains of suid herpesvirus 1
- PMID: 35733152
- PMCID: PMC9215027
- DOI: 10.1186/s13567-022-01063-8
Bartha-K61 vaccine protects nursery pigs against challenge with novel european and asian strains of suid herpesvirus 1
Abstract
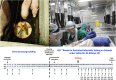
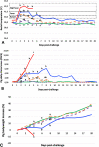
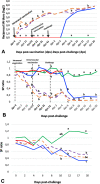
The present study investigates the pathogenicity of two recently isolated strains of Suid herpesvirus 1 (SuHV1), the Greek strain Hercules and the Chinese strain HeN1, in unvaccinated pigs and in pigs vaccinated with a Bartha-K61 strain. In an experiment performed in negative pressure kiosks (isolators), 45-day old seronegative pigs previously oronasally /intramuscularly vaccinated with the Bartha-K61 vaccine strain, along with unvaccinated controls, were challenged either with the Hercules strain or the HeN1 strain of SuHV1. All animals were observed daily for clinical signs and body temperature and nasal swabs, faeces, blood and bodyweight were collected up to a maximum period of 20 days post-challenge (dpc). The results showed that, in the unvaccinated pigs, HeN1 strain was more virulent than the Hercules strain, with increased mortality, shorter time to death and higher group clinical score (p < 0.05). However, after vaccination with the Bartha-K61 vaccine, there was a drastic reduction in morbidity, mortality, bodyweight loss and virus excretion to almost a similar extent in both strains (p < 0.05). No significant differences were seen among the pigs of the two vaccinated groups compared to unvaccinated unchallenged controls, except a slight elevation in body temperature and in clinical score in the HeN1 vaccinees at 2 and 3 dpc, while bodyweight gain was similar to that of the negative control pigs. Our study showed that despite differences in virulence, the standard vaccination scheme with the Bartha-K61 strain could equally protect nursery pigs against both the European and Chinese strains.
Keywords: Aujeszky’s disease; Bartha-K61 vaccine; Pseudorabies; pig; variant.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel pseudorabies virus variant with defects in TK, gE and gI protects growing pigs against lethal challenge.Vaccine. 2015 Oct 26;33(43):5733-5740. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.09.066. Epub 2015 Oct 1. Vaccine. 2015. PMID: 26428456
-
Pseudorabies virus variant in Bartha-K61-vaccinated pigs, China, 2012.Emerg Infect Dis. 2013 Nov;19(11):1749-55. doi: 10.3201/eid1911.130177. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 24188614 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of the Bartha-K61 vaccine and a gE-/gI-/TK- prototype vaccine against variant porcine pseudorabies virus (vPRV) in piglets with sublethal challenge of vPRV.Res Vet Sci. 2020 Feb;128:16-23. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2019.10.005. Epub 2019 Oct 25. Res Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 31707096
-
The Attenuated Pseudorabies Virus Vaccine Strain Bartha K61: A Brief Review on the Knowledge Gathered During 60 Years of Research.Pathogens. 2020 Oct 27;9(11):897. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9110897. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 33121171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Pseudorabies Virus Variants: Genomics, Vaccination, Transmission, and Zoonotic Potential.Viruses. 2022 May 9;14(5):1003. doi: 10.3390/v14051003. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35632745 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Immune Efficacy of Inactivated Pseudorabies Vaccine Prepared from FJ-2012ΔgE/gI Strain.Microorganisms. 2022 Sep 21;10(10):1880. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10101880. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36296157 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of immunogenicity of gene-deleted and subunit vaccines constructed against the emerging pseudorabies virus variants.Virol J. 2023 May 23;20(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s12985-023-02051-w. Virol J. 2023. PMID: 37221518 Free PMC article.
-
Additional Insertion of gC Gene Triggers Better Immune Efficacy of TK/gI/gE-Deleted Pseudorabies Virus in Mice.Viruses. 2024 Apr 29;16(5):706. doi: 10.3390/v16050706. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38793591 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular epidemiological and genetic characterization of pseudorabies virus in Guangxi, China.Arch Virol. 2023 Nov 8;168(12):285. doi: 10.1007/s00705-023-05907-2. Arch Virol. 2023. PMID: 37938380
References
-
- Mettenleiter TC, Ehlers B, Müller T, Yoon K-J, Teifke JP. Herpesviruses. In: Zimmerman JJ, Karriker LA, Ramirez A, Schwartz KJ, Stevenson GW, Zhang J, editors. Diseases of swine. 11. Hoboken: Wiley; 2019. pp. 548–575.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

