Lung function and exercise capacity 6 months after hospital discharge for critical COVID-19
- PMID: 35733179
- PMCID: PMC9215155
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-022-02023-w
Lung function and exercise capacity 6 months after hospital discharge for critical COVID-19
Abstract
Background: The significant morbidity caused by COVID-19 necessitates further understanding of long-term recovery. Our aim was to evaluate long-term lung function, exercise capacity, and radiological findings in patients after critical COVID-19.
Methods: Patients who received treatment in ICU for COVID-19 between March 2020 and January 2021 underwent pulmonary function tests, a 6MWD and CXR 6 months after hospital discharge.
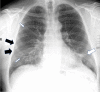
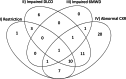
Results: A restrictive ventilatory defect was found in 35% (23/65) and an impaired diffusing capacity in 52% (32/62) at 6 months. The 6-minute walk distance was reduced in 33% (18/55), and 7% (4/55) of the patients had reduced exercise capacity. Chest X-ray was abnormal in 78% (52/67) at 6 months after hospital discharge.
Conclusion: A significant number of patients had persisting lung function impairment and radiological abnormalities at 6 months after critical COVID-19. Reduced exercise capacity was rare.
Keywords: ARDS; COVID-19; Critical care; Exercise capacity; Lung function.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. In the wake of the pandemic: preparing for long COVID. Policy Brief 39, 2021. https://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/health-emergencies/coronavirus.... Accessed 22 Sept 2021.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

