Single-cell RNA-seq reveals the genesis and heterogeneity of tumor microenvironment in pancreatic undifferentiated carcinoma with osteoclast-like giant-cells
- PMID: 35733218
- PMCID: PMC9214989
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-022-01596-8
Single-cell RNA-seq reveals the genesis and heterogeneity of tumor microenvironment in pancreatic undifferentiated carcinoma with osteoclast-like giant-cells
Abstract
Background: Undifferentiated carcinoma with osteoclast-like giant cells (OGCs) of pancreas (UCOGCP) is a rare subtype of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), which had poorly described histopathological and clinical features.
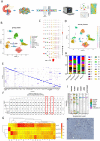
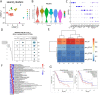
Methods: In this study, single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) was used to profile the distinct tumor microenvironment of UCOGCP using samples obtained from one UCOGCP patient and three PDAC patients. Bioinformatic analysis was carried out and immunohistochemical (IHC) staining was used to support the findings of bioinformatic analysis. After quality control of the raw data, a total of 18,376 cells were obtained from these four samples for subsequent analysis. These cells were divided into ten main cell types following the Seurat analysis pipeline. Among them, the UCOGCP sample displayed distinct distribution patterns from the rest samples in the epithelial cell, myeloid cell, fibroblast, and endothelial cell clusters. Further analysis supported that the OGCs were generated from stem-cell-like mesenchymal epithelial cells (SMECs).
Results: Functional analysis showed that the OGCs cluster was enriched in antigen presentation, immune response, and stem cell differentiation. Gene markers such as LOX, SPERINE1, CD44, and TGFBI were highly expressed in this SMECs cluster which signified poor prognosis. Interestingly, in myeloid cell, fibroblasts, and endothelial cell clusters, UCOGCP contained higher percentage of these cells and unique subclusters, compared with the rest of PDAC samples.
Conclusions: Analysis of cell communication depicted that CD74 plays important roles in the formation of the microenvironment of UCOGCP. Our findings illustrated the genesis and function of OGCs, and the tumor microenvironment (TME) of UCOGCP, providing insights for prognosis and treatment strategy for this rare type of pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: PDAC; Pancreatic cancer; Tumor microenvironment; UCOGCP; scRNA-seq.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures







Similar articles
-
The Survival Benefits of Chemotherapy for Undifferentiated Carcinoma With Osteoclast-Like Giant Cells of Pancreas: A Retrospective Analysis and Individual Participant Data Meta-Analysis.Cancer Med. 2025 May;14(9):e70894. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70894. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 40347088 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell transcriptome analysis reveals subtype-specific clonal evolution and microenvironmental changes in liver metastasis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma and their clinical implications.Mol Cancer. 2024 May 3;23(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02003-0. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38702773 Free PMC article.
-
Undifferentiated carcinoma with osteoclast-like giant cells of the pancreas: a narrative review.Front Oncol. 2024 Jun 19;14:1409197. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1409197. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38962271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Pancreatic Cancer Single-Cell Atlas Reveals Association of CXCL10+ Fibroblasts and Basal Subtype Tumor Cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Feb 17;31(4):756-772. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-2183. Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 39636224 Free PMC article.
-
Huge undifferentiated carcinoma of the pancreas with osteoclast-like giant cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Mar 14;20(10):2725-30. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i10.2725. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24627610 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Loss of Cadherin-11 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma alters tumor-immune microenvironment.Front Oncol. 2023 Oct 26;13:1286861. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1286861. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37954069 Free PMC article.
-
Progress of single-cell RNA sequencing combined with spatial transcriptomics in tumour microenvironment and treatment of pancreatic cancer.J Transl Med. 2024 Jun 12;22(1):563. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05307-3. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38867230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-Cell Sequencing-Based Validation of T Cell-Associated Diagnostic Model Genes and Drug Response in Crohn's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 23;24(7):6054. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076054. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047025 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic marker KRT81 is involved in suppressing CD8 + T cells and predicts immunotherapy response for triple-negative breast cancer.Cancer Biol Ther. 2024 Dec 31;25(1):2355705. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2024.2355705. Epub 2024 May 22. Cancer Biol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38778753 Free PMC article.
-
SPOCK1 promotes the progression of breast cancer by modulating cancer-associated fibroblasts and exerts a synergistic effect with ANXA2.Front Oncol. 2025 Aug 5;15:1619171. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1619171. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40837013 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reid MD, Muraki T, HooKim K, Memis B, Graham RP, Allende D, Shi J, Schaeffer DF, Singh R, Basturk O. Cytologic features and clinical implications of undifferentiated carcinoma with osteoclastic giant cells of the pancreas: an analysis of 15 cases. Cancer Cytopathol. 2017;125:563–575. doi: 10.1002/cncy.21859. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Maksymov V, Khalifa MA, Bussey A, Carter B, Hogan M. Undifferentiated (anaplastic) carcinoma of the pancreas with osteoclast-like giant cells showing various degree of pancreas duct involvement. A case report and literature review. JOP Journal of the Pancreas. 2011;12:170–176. - PubMed
-
- Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH, Theise ND. WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system. World Health Organization; 2010.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

