Performance of αSynuclein RT-QuIC in relation to neuropathological staging of Lewy body disease
- PMID: 35733234
- PMCID: PMC9219141
- DOI: 10.1186/s40478-022-01388-7
Performance of αSynuclein RT-QuIC in relation to neuropathological staging of Lewy body disease
Abstract
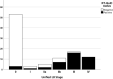
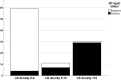
Currently, there is a need for diagnostic markers in Lewy body disorders (LBD). α-synuclein (αSyn) RT-QuIC has emerged as a promising assay to detect misfolded αSyn in clinically or neuropathologically established patients with various synucleinopathies. In this study, αSyn RT-QuIC was used to analyze lumbar CSF in a clinical cohort from the Swedish BioFINDER study and postmortem ventricular CSF in a neuropathological cohort from the Arizona Study of Aging and Neurodegenerative Disorders/Brain and Body Donation Program (AZSAND/BBDP). The BioFINDER cohort included 64 PD/PDD, 15 MSA, 15 PSP, 47 controls and two controls who later converted to PD/DLB. The neuropathological cohort included 101 cases with different brain disorders, including LBD and controls. In the BioFINDER cohort αSyn RT-QuIC identified LBD (i.e. PD, PDD and converters) vs. controls with a sensitivity of 95% and a specificity of 83%. The two controls that converted to LBD were αSyn RT-QuIC positive. Within the AZSAND/BBDP cohort, αSyn RT-QuIC identified neuropathologically verified "standard LBD" (i.e. PD, PD with AD and DLB; n = 25) vs. no LB pathology (n = 53) with high sensitivity (100%) and specificity (94%). Only 57% were αSyn RT-QuIC positive in the subgroup with "non-standard" LBD (i.e., AD with Lewy Bodies not meeting criteria for DLB or PD, and incidental LBD, n = 23). Furthermore, αSyn RT-QuIC reliably identified cases with LB pathology in the cortex (97% sensitivity) vs. cases with no LBs or LBs present only in the olfactory bulb (93% specificity). However, the sensitivity was low, only 50%, for cases with LB pathology restricted to the brainstem or amygdala, not affecting the allocortex or neocortex. In conclusion, αSyn RT-QuIC of CSF samples is highly sensitive and specific for identifying cases with clinicopathologically-defined Lewy body disorders and shows a lower sensitivity for non-standard LBD or asymptomatic LBD or in cases with modest LB pathology not affecting the cortex.
Keywords: Autopsy; Biomarkers; Cerebrospinal fluid; Dementia with Lewy bodies; Diagnosis; Lewy body dementia; Parkinson disease.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Figures

References
-
- (1997) Consensus recommendations for the postmortem diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. The National Institute on Aging, and Reagan Institute Working Group on Diagnostic Criteria for the Neuropathological Assessment of Alzheimer's Disease. Neurobiol Aging 18: S1–2 - PubMed

