CRISPR-mediated MECOM depletion retards tumor growth by reducing cancer stem cell properties in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 35733338
- PMCID: PMC9637721
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.06.011
CRISPR-mediated MECOM depletion retards tumor growth by reducing cancer stem cell properties in lung squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
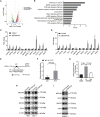
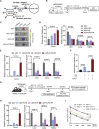
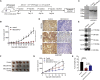
Targeted therapy for lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) remains a challenge due to the lack of robust targets. Here, we identified MECOM as a candidate of therapeutic target for LUSC by screening 38 genes that were commonly amplified in three pairs of primary tumors and patient-derived xenografts (PDXs) using a clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)-mediated approach. High MECOM expression levels were associated with poor prognosis. Forced expression of MECOM in LUSC cell lines promoted cancer stem cell (CSC) properties, and its knockout inhibited CSC phenotypes. Furthermore, systemic delivery of CRISPR-mediated MECOM depletion cassette using adenovirus with an adaptor, which is composed of a single-chain fragment variable (scFv) against epithelial cell adhesion molecules (EpCAM) fused to the ectodomain of coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor, and a protector, which consists of the scFv connected to the hexon symmetry of the adenovirus, could specifically target subcutaneous and orthotopic LUSC and retard tumor growth. This study could provide a novel therapeutic strategy for LUSC with high efficacy and specificity.
Keywords: CRISPR; MECOM; cancer stem cells; lung squamous cell carcinoma.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Genomic sequencing and editing revealed the GRM8 signaling pathway as potential therapeutic targets of squamous cell lung cancer.Cancer Lett. 2019 Feb 1;442:53-67. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.10.035. Epub 2018 Oct 27. Cancer Lett. 2019. PMID: 30391781
-
CRISPR-Cas9-mediated deletion enhancer of MECOM play a tumor suppressor role in ovarian cancer.Funct Integr Genomics. 2024 Jul 12;24(4):125. doi: 10.1007/s10142-024-01399-8. Funct Integr Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38995475
-
EVI1 Promotes the Proliferation and Invasive Properties of Human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 19;23(3):1050. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031050. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35162973 Free PMC article.
-
PAK5 promotes the cell stemness ability by phosphorylating SOX2 in lung squamous cell carcinomas.Exp Cell Res. 2020 Oct 15;395(2):112187. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.112187. Epub 2020 Jul 25. Exp Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 32721391
-
MECOM Deficiency: from Bone Marrow Failure to Impaired B-Cell Development.J Clin Immunol. 2023 Aug;43(6):1052-1066. doi: 10.1007/s10875-023-01545-0. Epub 2023 Jul 5. J Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37407873 Review.
Cited by
-
Risk stratification based on DNA damage-repair-related signature reflects the microenvironmental feature, metabolic status and therapeutic response of breast cancer.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 24;14:1127982. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1127982. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37033959 Free PMC article.
-
Cell states and neighborhoods in distinct clinical stages of primary and metastatic esophageal adenocarcinoma.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 3:2024.08.17.608386. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.17.608386. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Cell Rep Med. 2025 Jun 17;6(6):102188. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102188. PMID: 39229240 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The microprotein HDSP promotes gastric cancer progression through activating the MECOM-SPINK1-EGFR signaling axis.Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 27;15(1):8381. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50986-7. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39333095 Free PMC article.
-
Application of CRISPR screen in mechanistic studies of tumor development, tumor drug resistance, and tumor immunotherapy.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jun 23;11:1220376. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1220376. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37427373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring RNA cargo in extracellular vesicles for pleural mesothelioma detection.BMC Cancer. 2025 Feb 7;25(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13617-y. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39920655 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

