HLH-1 Modulates Muscle Proteostasis During Caenorhabditis elegans Larval Development
- PMID: 35733850
- PMCID: PMC9207508
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.920569
HLH-1 Modulates Muscle Proteostasis During Caenorhabditis elegans Larval Development
Abstract
Muscle proteostasis is shaped by the myogenic transcription factor MyoD which regulates the expression of chaperones during muscle differentiation. Whether MyoD can also modulate chaperone expression in terminally differentiated muscle cells remains open. Here we utilized a temperature-sensitive (ts) conditional knockdown nonsense mutation in MyoD ortholog in C. elegans, HLH-1, to ask whether MyoD plays a role in maintaining muscle proteostasis post myogenesis. We showed that hlh-1 is expressed during larval development and that hlh-1 knockdown at the first, second, or third larval stages resulted in severe defects in motility and muscle organization. Motility defects and myofilament organization were rescued when the clearance of hlh-1(ts) mRNA was inhibited, and hlh-1 mRNA levels were restored. Moreover, hlh-1 knockdown modulated the expression of chaperones with putative HLH-1 binding sites in their promoters, supporting HLH-1 role in muscle maintenance during larval development. Finally, mild disruption of hlh-1 expression during development resulted in earlier dysregulation of muscle maintenance and function during adulthood. We propose that the differentiation transcription factor, HLH-1, contributes to muscle maintenance and regulates cell-specific chaperone expression post differentiation. HLH-1 may thus impact muscle proteostasis and potentially the onset and manifestation of sarcopenia.
Keywords: Caenorhabditis elegans (c. elegans); MyoD; chaperone; development; hlh-1; myosin; proteostasis.
Copyright © 2022 Nisaa and Ben-Zvi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
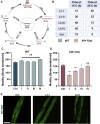

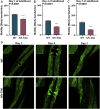
Similar articles
-
A Differentiation Transcription Factor Establishes Muscle-Specific Proteostasis in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS Genet. 2016 Dec 30;12(12):e1006531. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006531. eCollection 2016 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 28036392 Free PMC article.
-
The myogenic potency of HLH-1 reveals wide-spread developmental plasticity in early C. elegans embryos.Development. 2005 Apr;132(8):1795-805. doi: 10.1242/dev.01774. Epub 2005 Mar 16. Development. 2005. PMID: 15772130
-
The Caenorhabditis elegans MYOD homologue HLH-1 is essential for proper muscle function and complete morphogenesis.Development. 1994 Jun;120(6):1631-41. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.6.1631. Development. 1994. PMID: 8050369
-
Body-wall muscle formation in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos that lack the MyoD homolog hlh-1.Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):240-3. doi: 10.1126/science.1314423. Science. 1992. PMID: 1314423
-
MyoD and myogenesis in C. elegans.Bioessays. 1995 Mar;17(3):219-28. doi: 10.1002/bies.950170308. Bioessays. 1995. PMID: 7748176 Review.
Cited by
-
Decreased Hsp90 activity protects against TDP-43 neurotoxicity in a C. elegans model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.PLoS Genet. 2024 Dec 26;20(12):e1011518. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011518. eCollection 2024 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 39724103 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

