A Novel Maneuver to Treat Refractory Atelectasis in Mechanically Ventilated Children
- PMID: 35734215
- PMCID: PMC9208838
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0040-1721508
A Novel Maneuver to Treat Refractory Atelectasis in Mechanically Ventilated Children
Abstract
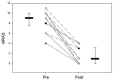
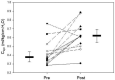
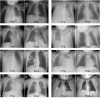
We developed a novel airway clearance and lung recruitment maneuver for children with refractory unilateral atelectasis undergoing invasive mechanical ventilation. In this retrospective, single-center, proof of concept study, we describe the steps involved in this novel maneuver and evaluate its effectiveness in 15 patients through objective quantitation of changes in respiratory system compliance and in the degree of atelectasis assessed by a validated Modified Radiology Atelectasis Score. Compared with the premaneuver baseline, the median atelectasis score improved significantly following the maneuver (9 [7.5-10] vs. 1 [0-3.3], respectively, p < 0.01). Likewise, dynamic compliance was significantly higher following the maneuver (0.3 [0.32-0.44] vs. 0.61 [0.53-0.69] mL/kg/cm H 2 O, respectively, p < 0.01). No patients required a bronchoscopy. This simple and effective maneuver resulted in a significant improvement in the degree of atelectasis and dynamic compliance in this cohort of mechanically ventilated children with refractory unilateral atelectasis.
Keywords: atelectasis; mechanical ventilation; pediatric critical care.
Thieme. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest A.T.R. reports personal fees from Vapotherm, Inc., personal fees from Breas U.S., personal fees from Elsevier, outside the submitted work. Rest of the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

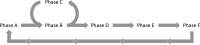
Similar articles
-
A comparison of intrapulmonary percussive ventilation and conventional chest physiotherapy for the treatment of atelectasis in the pediatric patient.Respir Care. 2002 Oct;47(10):1162-7. Respir Care. 2002. PMID: 12354335 Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of airway and a standardized recruitment maneuver on CT chest imaging quality in a pediatric population: A retrospective review.Paediatr Anaesth. 2022 Apr;32(4):572-576. doi: 10.1111/pan.14341. Epub 2021 Nov 29. Paediatr Anaesth. 2022. PMID: 34811851
-
Restoration of pulmonary compliance after laparoscopic surgery using a simple alveolar recruitment maneuver.J Clin Anesth. 2009 Sep;21(6):422-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2009.08.001. J Clin Anesth. 2009. PMID: 19833275
-
Atelectasis and lung recruitment in pediatric anesthesia: An educational review.Paediatr Anaesth. 2022 Feb;32(2):321-329. doi: 10.1111/pan.14335. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Paediatr Anaesth. 2022. PMID: 34797011 Review.
-
Recruitment maneuvers to reduce pulmonary atelectasis after cardiac surgery: A meta-analysis of randomized trials.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2022 Jul;164(1):171-181.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2020.10.142. Epub 2020 Nov 26. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2022. PMID: 33341273 Review.
Cited by
-
Refractory Atelectasis and Response to Chest Physiotherapy.J Pediatr Intensive Care. 2021 Jun 21;12(2):156-157. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1728640. eCollection 2023 Jun. J Pediatr Intensive Care. 2021. PMID: 37082467 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Refractory Atelectasis and Response to Chest Physiotherapy.J Pediatr Intensive Care. 2021 Jun 1;11(3):265-266. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1728639. eCollection 2022 Sep. J Pediatr Intensive Care. 2021. PMID: 35928040 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Structured respiratory physiotherapy protocol for resolution of atelectasis in pediatric intensive care.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2024 Sep 21;79:100494. doi: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2024.100494. eCollection 2024. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2024. PMID: 39306956 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Efficacy of Dornase Alpha (Polmozyme) in Resolving Persistent Atelectasis in Pediatric Critical Care.Cureus. 2025 Apr 20;17(4):e82655. doi: 10.7759/cureus.82655. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40400792 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thomas K, Habibi P, Britto J, Owens C M. Distribution and pathophysiology of acute lobar collapse in the pediatric intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 1999;27(08):1594–1597. - PubMed
-
- Al-Alaiyan S, Dyer D, Khan B. Chest physiotherapy and post-extubation atelectasis in infants. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1996;21(04):227–230. - PubMed
-
- Marini J J. Acute lobar atelectasis. Chest. 2019;155(05):1049–1058. - PubMed
-
- Kavanagh B P. Perioperative atelectasis. Minerva Anestesiol. 2008;74(06):285–287. - PubMed
-
- Deakins K, Chatburn R L. A comparison of intrapulmonary percussive ventilation and conventional chest physiotherapy for the treatment of atelectasis in the pediatric patient. Respir Care. 2002;47(10):1162–1167. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

