Evaluation of Expanded Criteria Donors Using the Kidney Donor Profile Index and the Preimplantation Renal Biopsy
- PMID: 35734238
- PMCID: PMC9207180
- DOI: 10.3389/ti.2022.10056
Evaluation of Expanded Criteria Donors Using the Kidney Donor Profile Index and the Preimplantation Renal Biopsy
Abstract
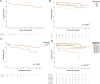
The increasing comorbidity of kidney transplant (KT) donors make it necessary to develop scores to correctly assess the quality of kidney grafts. This study analyzes the usefulness of the preimplantation biopsy and the Kidney Donor Profile Index (KDPI) as indicators of KT survival from expanded criteria donors (ECD). Retrospective study of KT in our center between January 2010 to June 2019 who received a kidney from an ECD and underwent a preimplantation biopsy. 266 KT were included. Graft survival was categorized by KDPI quartiles: Q1 = 86%, Q2 = 95%, Q3 = 99% and Q4 = 100%. KT from KDPI Q1 presented better survival (p = 0.003) and Q4 donors had worse renal function (p = 0.018) and poorer glomerular filtration rate (3rd month; p = 0.017, 1st year; p = 0.010). KT survival was analyzed according to KDPI quartile and preimplantation biopsy score simultaneously: Q1 donors with biopsy score ≤3 had the best survival, especially comparing against Q3 with a biopsy score >3 and Q4 donors (p = 0.014). In multivariable analysis, hyaline arteriopathy, glomerulosclerosis, and KDPI Q4 were predictors for graft survival. High KDPI and a greater histological injury in the preimplantation biopsy, especially glomerular and vascular lesions, were related to a higher rate of KT loss from ECD.
Keywords: expanded criteria donors; graft survival; kidney donor profile index; kidney transplantation; preimplantation biopsy.
Copyright © 2022 Villanego, Vigara, Cazorla, Naranjo, Atienza, Garcia, Montero, Minguez, Garcia and Mazuecos.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- National Transplant Organization. Donation and Transplant Activity Reports [Internet] (2020). Available from: http://www.ont.es/infesp/Memorias/Actividad_de_Donaci%C3%B3n_y_Trasplant... (Accessed June 12, 2021).

