Neural substrates of brand equity: applying a quantitative meta-analytical method for neuroimage studies
- PMID: 35734557
- PMCID: PMC9207674
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09702
Neural substrates of brand equity: applying a quantitative meta-analytical method for neuroimage studies
Abstract
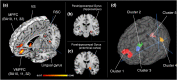
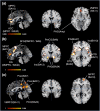
Although the concept of brand equity has been investigated using various approaches, a comprehensive neural basis for brand equity remains unclear. The default mode network (DMN) as a mental process might influence brand equity related consumers' decision-making, as reported in the marketing literature. While studies on the overlapping regions between the DMN and value-based decision-making related brain regions have been reported in neuroscience literature, relationships between the DMN and a neural mechanism of brand equity have not been clarified. The aim of our study is to identify neural substrates of brand equity and examine brand equity-related mental processes by comparing them to the DMN. To determine the neural substrates of brand equity, we first carried out the activation likelihood estimation (ALE) meta-analysis. We examined 26 studies using branded objects as experimental stimuli for the ALE. Next, we set the output regions from ALE as the region of interest for meta-analytic connectivity modeling (MACM). Further, we compared the brand equity-related brain network (BE-RBN) revealed by the MACM with the DMN. We confirmed that the BE-RBN brain regions overlap with the medial temporal lobule (MTL) sub-system, a module composed of the DMN but excluding the retrosplenial cortex. Further, we discovered that several brain regions apart from the DMN are also distinctive BE-RBN brain regions (i.e., the insula, the inferior frontal gyrus, amygdala, ventral striatum, parietal region). We decoded the BE-RBN brain regions using the BrandMap module. The decoded results revealed that the brand equity-related mental processes are complex constructs integrated via multiple mental processes such as self-referential, reward, emotional, memory, and sensorimotor processing. Our study demonstrated that the DMN alone is insufficient to engage in brand equity-related mental processes. Therefore, marketers are required to make strategic plans to integrate the five consumer's multiple mental processes while building brand equity.
Keywords: ALE; Brand management; Consumer decision making; Consumer neuroscience; DMN; Neuromarketing; fMRI.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Aaker D.A. The Free Press; New York: 1996. Building Strong Brands.
-
- Aaker D.A. The value of brand equity. J. Bus. Strat. 1992;13:27–32.
-
- Addis D.R., McAndrews M.P. Prefrontal and hippocampal contributions to the generation and binding of semantic associations during successful encoding. Neuroimage. 2006;33:1194–1206. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

