Radiomic Signatures for Predicting Receptor Status in Breast Cancer Brain Metastases
- PMID: 35734585
- PMCID: PMC9207517
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.878388
Radiomic Signatures for Predicting Receptor Status in Breast Cancer Brain Metastases
Abstract
Backgrounds: A significant proportion of breast cancer patients showed receptor discordance between primary cancers and breast cancer brain metastases (BCBM), which significantly affected therapeutic decision-making. But it was not always feasible to obtain BCBM tissues. The aim of the present study was to analyze the receptor status of primary breast cancer and matched brain metastases and establish radiomic signatures to predict the receptor status of BCBM.
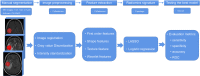
Methods: The receptor status of 80 matched primary breast cancers and resected brain metastases were retrospectively analyzed. Radiomic features were extracted using preoperative brain MRI (contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging, T2-weighted imaging, T2 fluid-attenuated inversion recovery, and combinations of these sequences) collected from 68 patients (45 and 23 for training and test sets, respectively) with BCBM excision. Using least absolute shrinkage selection operator and logistic regression model, the machine learning-based radiomic signatures were constructed to predict the estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) status of BCBM.
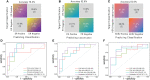
Results: Discordance between the primary cancer and BCBM was found in 51.3% of patients, with 27.5%, 27.5%, and 5.0% discordance for ER, PR, and HER2, respectively. Loss of receptor expression was more common (33.8%) than gain (18.8%). The radiomic signatures built using combination sequences had the best performance in the training and test sets. The combination model yielded AUCs of 0.89, 0.88, and 0.87, classification sensitivities of 71.4%, 90%, and 87.5%, specificities of 81.2%, 76.9%, and 71.4%, and accuracies of 78.3%, 82.6%, and 82.6% for ER, PR, and HER2, respectively, in the test set.
Conclusions: Receptor conversion in BCBM was common, and radiomic signatures show potential for noninvasively predicting BCBM receptor status.
Keywords: brain neoplasms; breast neoplasms; magnetic resonance imaging; radiomics; receptor.
Copyright © 2022 Luo, Xie, Yang, Zhang, Zhang, Li, Yang, Wang, Luo, Mai, Xie and Yin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Timmer M, Werner JM, Rohn G, Ortmann M, Blau T, Cramer C, et al. Discordance and Conversion Rates of Progesterone-, Estrogen-, and Her2/Neu-Receptor Status in Primary Breast Cancer and Brain Metastasis Mainly Triggered by Hormone Therapy. Anticancer Res (2017) 37(9):4859–65. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.11894 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

