Management of trauma White weapons penetrating Head and Neck in the anesthesia department of the national hospital of Zinder in Niger: About five reported cases
- PMID: 35734682
- PMCID: PMC9207114
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103840
Management of trauma White weapons penetrating Head and Neck in the anesthesia department of the national hospital of Zinder in Niger: About five reported cases
Abstract
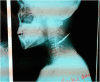
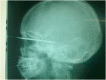
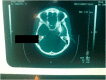
We report five cases of craniocervical trauma with knives. The occurrence circumstances were common to all injuries. The trauma was caused by a knife during a fight or an intentional injury. All the victims were farmers or ranchers. Their average age was 17 years, with extremes of 13 and 22 years. The cause was most often community conflict. Pre-hospital transport was non-medical for all patients. The average admission time was 3 h and the average management time was 4 h. General anesthesia with orotracheal intubation was the anesthetic technique used. The average length of hospital stay was seven days. The prognosis was overall favorable and the patients returned home without any sequels.
Keywords: And neck; Head; Knives; Management; Niger; Penetrating injuries.
© 2022 Published by Elsevier Ltd on behalf of IJS Publishing Group Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interests.
Figures








References
-
- G. E Gmann et al. Stab Wounds. Sfmu URGENCES 2010 437-456.
-
- Eachempati S.R., Barie P.S., Reed R.L., 2nd Survival after transabdominal impalement from a construction injury: a review of the management of impalement injuries. J. Trauma. 1999;47:864–866. - PubMed
-
- V. Mardelle, A. de Waroquier, A. Nau, E. Peytel. PENETRATING TRAUMA TO THE SAUSAGE.
-
- Kaboro M, Djonga O, Djadda D, et al. Human Violence Injuries: a Public Health Problem in N'Djamena (Chad). Ann Univ Ndj, (C2):114-127. 2007: Multiple Myeloma, Plasmacytosis, Monoclonal Peak, Remission, N.
-
- Monneuse O.J., Barth X., Gruner L., et al. Penetrating wounds of the abdomen: diagnosis and treatment. About 79 cases. Ann. Chir. 2004;129:156–163. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

