Multiple primary pulmonary meningioma: A case report and literature review
- PMID: 35734847
- PMCID: PMC9346167
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.14542
Multiple primary pulmonary meningioma: A case report and literature review
Abstract
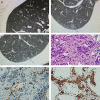
Lung cancer has become a leading cause of cancer-related deaths. With the conventional use of low-dose spiral computed tomography (CT) in physical examinations, an increasing number of small pulmonary nodules are screened. However, primary pulmonary meningiomas (PPMs) are rarely reported. Here, we report the case of a 64-year-old woman who had a CT scan during physical examination, which revealed three ground-glass-like opacity pulmonary nodules in both lungs. The patient underwent video-assisted thoracoscopic wedge resection of the right upper and lower lobes. Paraffin sections revealed pulmonary meningothelial-like and collagenous nodules in the right upper and lower lobes which stained as follows: EMA+, VIM+, SMA-, S-100-, CD34-, STAT6-, Ki-67+ (2%), and CgA-. Primary pulmonary meningiomas (PPMs) were finally diagnosed. PPM is a kind of rare and benign tumor. Surgery can provide a precise pathological examination, and patients can achieve an excellent prognosis after surgical resection.
© 2022 The Authors. Thoracic Cancer published by China Lung Oncology Group and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Weis A, Philippides D, Montrieul B, Steimle R. Primary pulmonary meningioma: a rare, slow‐growing tumor. Radiol Electrol Arch Electr Medicale. 1952;4:701–3. - PubMed
-
- Kenmitz P, Spormann H, Heinrich P. Meningioma of lung:first report with light and electron microscopic findings. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1982;3(4):359–65. - PubMed
-
- Prayson RA, Farver CF. Primary pulmonary malignant meningioma. Am J Surg Pathol, 1999, 23(6): 722–726. - PubMed
-
- Van der Meij JJ, Boomars KA, van den Bancosch JM, Van Boven WJ, De Bruin PC, Seldenrijk CA. Primary pulmonary malignant meningioma. Ann Thorac Surg, 2005, 80(4): 1523–1525. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

