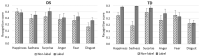Recognition of Basic Emotions with and without the Use of Emotional Vocabulary by Adolescents with Down Syndrome
- PMID: 35735377
- PMCID: PMC9220526
- DOI: 10.3390/bs12060167
Recognition of Basic Emotions with and without the Use of Emotional Vocabulary by Adolescents with Down Syndrome
Abstract
Background: Children with Down syndrome (DS) often experience behavioral and emotional issues that complicate their socialization process and may lead to psychopathological disorders. These problems may be related to deficits affecting emotional knowledge, particularly emotional vocabulary. Because emotional vocabulary makes it easier for typically developing children to identify emotions, a deficit affecting it in DS could be problematic.
Methods: Twenty-eight adolescents with DS matched with typically developing (TD) children for their score on the Benton Facial Recognition Test were asked to recognize six emotional expressions presented in the form of filmed sequences, based on (1) nonverbal cues such as prosody, and (2) an emotional label.
Results: The adolescents with DS recognized the six basic emotional expressions at a level comparable to that of the TD children in both conditions (with and without emotional vocabulary), but the facilitating effect of vocabulary was lower in that group.
Conclusions: This study does not show a deficit affecting emotion recognition in DS, but it emphasizes the importance of early acquisition of emotional knowledge in this syndrome. Regular and varied use of internal state words should be encouraged in familial interactions, and education should include specifically adapted social and emotional learning programs.
Keywords: down syndrome; emotion recognition; emotional competence; emotional vocabulary.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emotion Recognition in Adolescents with Down Syndrome: A Nonverbal Approach.Brain Sci. 2017 May 23;7(6):55. doi: 10.3390/brainsci7060055. Brain Sci. 2017. PMID: 28545237 Free PMC article.
-
How Individuals With Down Syndrome Process Faces and Words Conveying Emotions? Evidence From a Priming Paradigm.Front Psychol. 2020 Apr 17;11:692. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00692. eCollection 2020. Front Psychol. 2020. PMID: 32362859 Free PMC article.
-
Emotional Lexicon in Down Syndrome.Am J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2022 Jul 1;127(4):278-292. doi: 10.1352/1944-7558-127.4.278. Am J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2022. PMID: 36122328
-
Recognition of emotional facial expressions in adolescents with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder.J Adolesc. 2020 Jul;82:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.adolescence.2020.04.010. Epub 2020 May 19. J Adolesc. 2020. PMID: 32442797 Review.
-
Congenital facial palsy and emotion processing: The case of Moebius syndrome.Genes Brain Behav. 2019 Jan;18(1):e12548. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12548. Genes Brain Behav. 2019. PMID: 30604920 Review.
Cited by
-
Differences in pragmatic communication skills of adults with intellectual disabilities and dual diagnoses.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Feb 2;14:1072736. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1072736. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36816408 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Iarocci G., Yager J., Rombough A., McLaughlin J. The development of social competence among persons with Down syndrome: From survival to social inclusion. Int. Rev. Res. Ment. Retard. 2008;35:87–119. doi: 10.1016/S0074-775035003-9. - DOI
-
- Fidler D., Most D., Philofsky A. The Down syndrome behavioural phenotype: Taking a developmental approach. Down Syndr. Res. Pract. 2008;12:37–44. doi: 10.3104/reviews/2069. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources